How Will The East Coast Main Line Timetable Change Affect Sheffield?
This article in the October 2025 Edition of Modern Railways is entitled Industry Gears Up For December ECML Timetable Change.
This is the first paragraph.
Major changes are planned to trains along the East Coast main line from 14 December as the long-heralded timetable takes effect.
In this post, I will see how the changes detailed in the article in Modern Railways will affect Sheffield and Doncaster.
Aberdeen-Edinburgh
This is said about Aberdeen and Edinburgh services.
Monday-Saturday services will not change between Aberdeen and Edinburgh, with all intermediate stations served at similar times.
The LNER service to and from King’s Cross will call additionally at Doncaster, Newark Northgate and Peterborough; the last LNER Monday-Friday departure from Aberdeen will terminate at Doncaster instead of Leeds, and the first LNER Monday-Saturday train to Aberdeen will start from King’s Cross at 05:48 instead of Leeds.
Note.
- An hourly fast train between Edinburgh and King’s Cross will have a journey time of 4 hours and 10 minutes, which is a saving of at least 12 minutes.
- There is an Aberdeen-Manchester air service, but no Edinburgh-Manchester or Leeds-Scotland air services.
- In Could London And Central Scotland Air Passengers Be Persuaded To Use The Trains?, I speculated about how air passengers could be tempted to use the trains between London and Central Scotland.
- It looks to me, that LNER are strengthening their services between Doncaster and Scotland.
- Will that 05:48 King’s Cross departure for Aberdeen, enable a working day in Aberdeen and return?
Is LNER’s aim to get travellers to use the trains between Doncaster and Scotland, as an alternative to driving or trains from Leeds?
Alnmouth and Berwick
This is said about Alnmouth services.
Quicker LNER journey times are promised to stations South of York, with King’s Cross-Alnmouth journey times up to 15 minutes quicker.
More TPE trains will run between Newcastle, Morpeth, Alnmouth, Berwick, Reston, Dunbar, East Linton and Edinburgh Waverley.
The number of trains calling at Durham on weekdays will fall from 18 to 13 Southbound and from 15 to 10 Northbound.
This is said about Berwick services.
LNER trains will call every two hours during the middle of the day, and the number of weekday trains to King’s Cross falls from 15 to 11 Southbound with a 13 to nine fall Northbound. More TPE trains will call.
Note.
- Lumo serves Newcastle, Morpeth and Edinburgh.
- Reston and East Linton are new stations.
- The stations between Newcastle and Edinburgh need adequate parking to attract commuters.
It looks to me, that LNER are timing the trains to attract day trips along the East Coast Main Line.
Bradford Forster Square/Interchange
This is said about Bradford Forster Square services.
The number of weekday trains will remain as per May 2025, but on Sundays, the number of trains serving Forster Square increases from two to six each way on a two-hourly interval. LNER stopping patterns change, with fewer trains calling at Peterborough and none at Grantham or Retford.
Trains currently stop at Peterborough, Doncaster, Wakefield Westgate, Leeds and Shipley, but surely a more regular six trains per day (tpd) is preferable.
This is said about Bradford Interchange services.
At Interchange, Grand Central Trains will run at different times to the May 2025 timetable, with King’s Cross journeys up to 20 minutes quicker. One GC each way will call at Peterborough, while some will stop at Pontefract Monkhill on Sundays for the first time.
Note.
- Trains currently stop at Peterborough, Doncaster, Pontefract Monkhill, Wakefield Kirkgate, Mirfield, Brighouse, Halifax and Low Moor
- Is the twenty minutes time saving due to the new digital signalling to the South of Doncaster?
- Is this another open access operator being allowed to do what they do best?
This looks to be a very useful service, which serves several stations, with no other service to London.
Doncaster
This is said about Doncaster services.
Additional trains calling at destinations including Birmingham New Street, Sheffield, York, Newark and Berwick-upon-Tweed. LNER Aberdeen/Inverness trains will call at Doncaster. EMR trains will be retimed at Doncaster to provide better connections with LNER’s revised timetables, but journeys from Doncaster to Sleaford and Spalding will require a change at Lincoln. This change has been made to “enable improved connections” at Peterborough, Sleaford, Lincoln and Doncaster. The number of trains calling at Stevenage falls from 24 to 19 Southbound and 24 to 21 Northbound, with Grantham stops dropping by seven trains to 28 Southbound and 4 to 29 Northbound.
If CrossCountry Trains were to switch their trains to Hitachi InterCity Battery trains, I believe that a version of these trains could handle routes like Plymouth and Aberdeen.
- This would speed up services.
- Trains would run close together and thus increase capacity.
- Services could even be faster.
So expect a replacement order for CrossCountry Trains diesel multiple units soon.
Glasgow
LNER gave up serving Glasgow Central from King’s Cross in the December 2024 timetable change.
In Lumo Will Extend Its King’s Cross And Edinburgh Service To Glasgow, I talked about Lumo extending their King’s Cross and Edinburgh service to Glasgow Central station.
Hull
This is said about Hull services.
On Mondays-Fridays, Hull Trains will provide an extra train from London.
The LNER Monday-Friday Hull-Doncaster train will be withdrawn;
Northern will operate a 20:25 departure to Doncaster; calling at Brough and Selby.
Note.
- It looks like Great British Railways have surrendered Hull and Beverley to Hull Trains.
- Hull Trains are converting their Class 802 trains to battery-electric power.
- It is likely that Hull Trains upgraded trains will be able to use the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line via Lincoln on battery power.
The new timetable appears to be ready for the future of Hull Trains.
Leeds
This is said about Leeds services.
LNER services will depart to King’s Cross at xx.10 and xx.40.
Northern will introduce an extra mostly hourly service between Leeds and Sheffield calling at Wakefield Westgate. They will depart about 30 minutes earlier or later than the CrossCountry service.
Note.
- I would expect the two King’s Cross and Leeds services which would both stop at Doncaster and Wakefield Westgate would set the timings between Doncaster and Leeds.
- Currently, of the four trains that run to and from Leeds every two hours, two are planned to terminate at Leeds, one at Harrogate and one at Bradford Forster Square.
- There is also a daily service between King’s Cross and Skipton via Leeds.
- I can envisage another service between King’s Cross and Ilkley via Leeds, Kirkstall Forge, Guiseley, Burley-in-Wharfedale and Ben Rhydding.
- I can envisage another service between King’s Cross and Huddersfield, via Leeds, White Rose, Morley, Batley, Dewsbury, Ravensthorpe, Mirfield and Deighton.
- I can envisage another service between King’s Cross and Hebden Bridge, via Leeds, White Rose, Morley, Batley, Dewsbury, Ravensthorpe, Mirfield, Sowerby Bridge, Mytholmroyd and Brighouse.
- An alternative to Hebden Bridge would be Rochdale, which already has four platforms and is on the Manchester Metrolink
- It appears that Bradford Forster Square, Harrogate, Huddersfield, Leeds and Skipton stations can turn nine or ten-car trains and Ilkley can turn five-car trains.
- I also believe that one of Hitachi’s InterCity Battery trains could use battery power to take the spectacular Settle and Carlisle Line to Carlisle or even Glasgow Central.
- If needed pairs of five-car trains could split and join at Leeds, with one train waiting at Leeds and the other train going on to another destination.
- The CrossCountry and Northern Trains services on the Sheffield and Leeds route via Doncaster and Wakefield Westgate would probably need to be modern battery-electric trains to maximise the capacity on the route.
There certainly seem to be opportunities to give a number of stations in Yorkshire an all-electric service to King’s Cross with a two-hourly frequency, in a time of a few minutes over two hours.
Lincoln
This is said about Lincoln services.
One more LNER train from King’s Cross will run, with the first train arriving earlier and the last train later. There will no longer be an LNER train serving Stevenage with passengers having to change at Newark Northgate or Peterborough. An improved service will run to and from Nottingham, with an increase from one to two trains per hour on Mondays-Saturdays. An hourly service will run to Crewe, and a new Matlock-Nottingham-Lincoln-Cleethorpes service will run. EMR will cease all bar morning peak direct trains to/from Leicester. Newark Northgate-Lincoln trains will be reduced from five to four on Mondays-Fridays, eight to four on Saturdays and ten to eight on Sundays.
Note.
- Travellers between Lincoln/Nottingham and the North/Scotland will have two trains per hour to Newark Northgate, where there will be two tph to the North/Scotland.
- The hourly Crewe service will give access to Liverpool Manchester and the West Coast Main Line.
- Will there still be a Liverpool and Norwich service or will this be replaced by East-West Rail?
There seems to be a big sort out to EMR services.
Newcastle
This is said about Newcastle services.
The number of trains serving King’s Cross increases from 35 to 53 Southbound on weekdays and from 36 to 52 Northbound. One train every hour will run non-stop to York. More TPE trains will run Northbound (see Alnmouth and Berwick), while Northern is retiming services on the Northumberland Line in anticipation of Northumberland Park and Bedlington stations opening in early 2026. A semi-fast hourly service between Newcastle and Middlesbrough will run on Mondays-Saturdays and there will be an hourly stopping service between them.
Note.
- There will be a big increase in services between King’s Cross and Newcastle.
- Is the aim to persuade travellers to use trains rather than airlines?
- LNER also runs one train per day (tpd) between King’s Cross and Middlesbrough.
- Grand Central Trains will be running at a frequency of six tpd between King’s Cross and Sunderland via Thirsk, Northallerton, Eaglescliffe, Hartlepool and Seaham.
Hull appears to have been left to Hull Trains and Glasgow to Lumo, and Sunderland appears to be left for Grand Central Trains.
Conclusions
I am coming to some conclusions about services on the East Coast Main Line, with respect to Sheffield.
Doncaster Is A Well-Equipped Station
Doncaster is the nearest station to Sheffield on the East Coast Main Line.
- Over the last few years, Doncaster station has been improved.
- It has a subway with a more than adequate number of lifts.
- The station has nearly 600 parking spaces.
- There is a taxi rank.
- There is no Marks & Spencer’s food store, which is important for a coeliac like me.
- There are thirty bus stands close to Doncaster station.
- Doncaster station is well-equipped with cafes, a pub and coffee stalls.
- All trains to Aberdeen, Bradford Forster Square, Bradford Interchange, Edinburgh, Hull, King’s Cross, Leeds, Sheffield and Wakefield seem to stop at the station.
- There are several local trains per hour.
- Changing trains is not a strenuous exercise.
Doncaster is one of the UK’s better regional stations.
Doncaster Needs A Connection To The Sheffield Supertram
One of the first things, I do when I arrive in a strange town or city is look for the local public transport network.
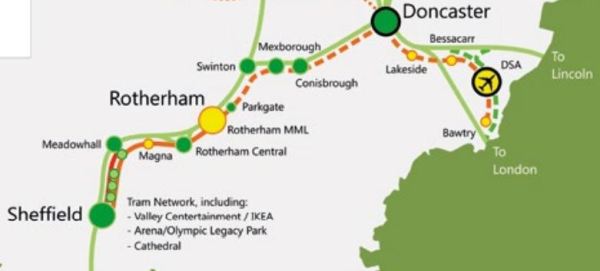
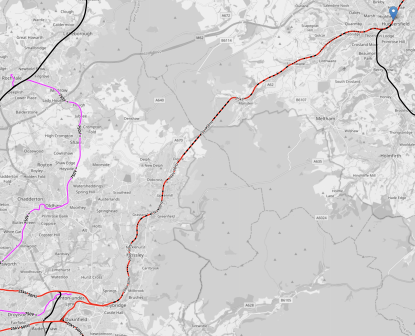
In 2019, Sheffield published an ambitious plan for their tram network, which I wrote about in Sheffield Region Transport Plan 2019 – Doncaster Sheffield Airport.
The post contained this map, of Sheffield’s plans for the trams.
Doncaster and Doncaster Sheffield Airport are connected to the current end of the tram-train route at Rotherham Parkgate.
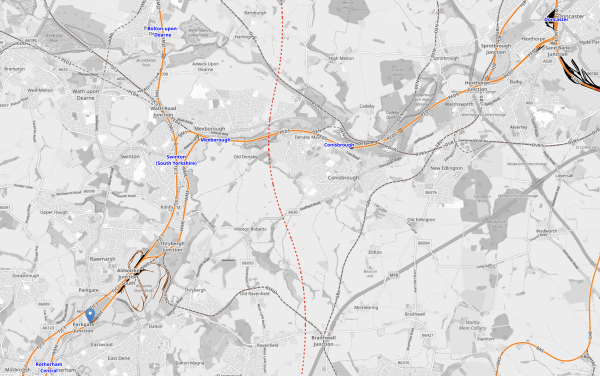
This OpenRailwayMap shows the rail lines between Rotherham Parkgate and Doncaster.
Note.
- Doncaster station is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Rotherham Central station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The blue arrow in the South-West corner indicates Rotherham Parkgate tram stop.
- Swinton, Mexborough and Conisbrough stations can be picked out.
- The dotted red line running North-South across the map is the route of the ill-fated Eastern Leg of High Speed Two.
It is a simple application of tram-train technology to connect Doncaster station and Doncaster Sheffield Airport to the Sheffield Supertram.
With all the comings and goings on the East Coast Main Line at Doncaster station, I believe that the tram-train connection to Sheffield and Rotherham is essential.
The Cities Of Bradford, Doncaster, Leeds, Sheffield and Wakefield Can Have a High-Frequency Rail Connection
Consider.
- Four stations are all step-free with a bridge or subway served by lifts.
- Bradford Forster Square station has level access to the platforms from the street.
- The rail lines between the five stations are electrified, with the exception of Sheffield and Doncaster.
- Services between the cities are run by CrossCountry Trains, Grand Central Trains, Hull Trains, LNER and Northern Trains.
- Most maximum speeds are not unduly slow.
Consequently the five cities can have a high-frequency rail connection in excess of four tph.
Could this be the basis of a Five-Cities Metro?
Open Access Services
There are six open access services running on the East Coast Main Line.
- Grand Central Trains – King’s Cross-Bradford Interchange via Peterborough, Doncaster, Pontefract Monkhill, Wakefield Kirkgate, Mirfield, Brighouse, Halifax and Low Moor – 4 tpd
- Grand Central Trains – King’s Cross-Sunderland via Peterborough, York, Thirsk, Northallerton, Eaglescliffe and Hartlepool – 6 tpd
- Hull Trains – King’s Cross-Hull via Stevenage, Grantham, Retford, Doncaster, Selby, Howden, Brough – 4 tpd
- Hull Trains – King’s Cross-Beverley via Stevenage, Grantham, Retford, Doncaster, Selby, Howden, Brough, Hull and Cottingham – 2 tpd
- Lumo – King’s Cross-Edinbugh via Stevenage, Newcastle and Morpeth – 5 tpd
- Lumo – King’s Cross-Glasgow Queen Street via Stevenage, Newcastle, Morpeth, Edinburgh and Falkirk High – 2 tpd
Note.
- tpd is trains per day.
- All seem to serve an exclusive area, except Lumo.
- In a couple of years, all could be using Hitachi trains.
- I suspect some services will swap their diesel generators for batteries.
Battery-power would allow some services to be zero-carbon, even when using the GNGE diversion.
I’ve Just Glimpsed The Future Of Train Travel Across The North Of England And I Like It
Yesterday, I had an appointment at Liverpool Lime Street station at four o’clock, so as I hadn’t seen the works for the TransPennine Upgrade for some time, I decided to go the long way round with a change of train from LNER to TransPennine Express at Leeds.
These sections document my day.
London King’s Cross To Leeds In An InterCity 225
I took these pictures on the journey.
Note.
- The 31 InterCity 225 trains were built around 1990.
- They have a capacity of 535 seats, whereas the newer Hitachi Class 801 trains have a capacity of 611 seats. Both trains are nine cars with both First and Standard seats.
- There is more of a step-up and step-down when entering or leaving the trains, compared to the best of today’s trains.
- They are now being phased out in favour of ten new CAF tri-mode Class 897 trains, which should be entering service in 2027.
- No details are available of the seating capacity of these trains, but they could be between 650 and 700, so they could maximise capacity on any LNER route.
Yesterday, the InterCity 225 performed well, although the windows at the seat where I sat, were rather dirty.
Changing Trains At Leeds Station
I changed to TransPennine Exzpress at Leeds station.
- At least, Leeds station, is one of the few in the UK, with a ticket office behind the barrier. Reading station please note this.
- But, I did have to walk across the bridge from one side of the station to the other.
In the end, I caught the TransPennine Express with about thirty seconds to spare.
Between Leeds And Huddersfield Stations
I took these pictures between Leeds and Huddersfield stations.
Note.
- Dewsbury and Huddersfield stations is about eight miles and takes about eight minutes.
- It is virtually a continuous building site, where extra tracks are being inserted.
- Three stations are being rebuilt.
- Overhead electrification is being installed. But except for approaching Huddersfield, there’s not much to be seen.
- OpenRailwayMap gives the maximum speed between Dewsbury and Huddersfield stations as between 60-75 mph.
The ride on my Class 803 train was very quiet and smooth. Was it on battery power or was I sitting in a coach without a diesel engine underneath?
Huddersfield Station
I took these pictures at Huddersfield station.
Note.
- Huddersfield station is Grade I Listed.
- There is a pub in each wing.
- I had a beer in the West Wing.
- There are currently three main through platforms and three bay platforms.
- Extensive works, which will be part of the TransPennine Upgrade, will include electrification, a new roof, a new footbridge, and two extra through platforms.
Huddersfield station will be the jewel in the Costa del Yorkshire.
The Platforms At Huddersfield Station
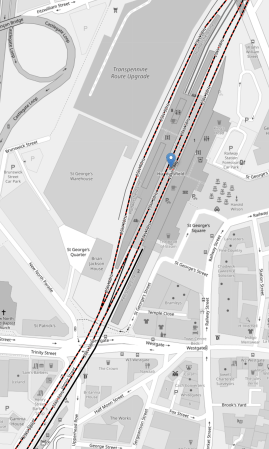
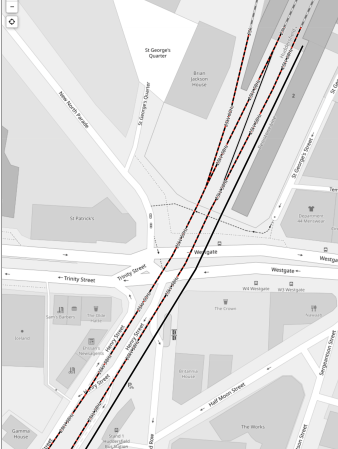
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms in Huddersfield station.
Note.
- The red and black tracks are being electrified.
- Of the current platforms, Platforms 1, 4 and 8 will be electrified.
- The two bay platforms; 5 and 6, will be converted into through platforms.
- Platform 2 is the bay platform in the South-West corner of the map, that is used by the shuttle train from Sheffield.
I am sure extra platforms could be electrified as required, as there must be a good electrical connection at Huddersfield station.
A Tram-Train Service Between Huddersfield And Sheffield Stations
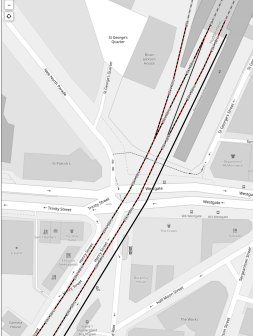
This OpenRailwayMap shows platform 2 at Huddersfield station.
Note.
- Platform 2 is the black track at the right of the two through tracks, that are being electrified.
- Platform 2 is a bay platform close to the Head of Steam pub.
- I estimate that the platform is about 90 metres long.
- I suspect Platform 2 could be lengthened if required.
- Sheffield’s Class 399 tram/trains are 37.2 metres long, so a pair should fit in Platform 2.
- The Class 398 tram/trains can run on battery power and climb hills in South Wales.
- Platform 2 at Huddersfield station could be electrified to charge the tram/trains.
- There could be a significant height difference between Huddersfield and Sheffield stations of about 40 metres, which could be used to charge tram/trains on the way down.
- I feel with some track improvements, that a four trains per hour (tph) service could be run.
The service would call at Meadowhall, Chapeltown, Elsecar, Wombwell, Barnsley, Dodworth, Silkstone Common, Penistone, Denby Dale, Shepley, Stocksmoor, Brockholes, Honley, Berry Brow and Lockwood
The Pair Of Cranes In Huddersfield Station
These can’t be missed in the pictures. But why two massive cranes?
With an old roof to be taken down and a new roof and a footbridge to be lifted into place, I believe Network Rail have decided to bring in two of largest mobile cranes available in the UK, so that all the lifting doesn’t delay the project.
Between Huddersfield And Stalybridge Stations
I took these pictures between Huddersfield and Stalybridge stations.
Note.
- The Class 802 train was running freely along a well-laid track.
- There are four stations between Huddersfield and Stalybridge; Slaithwaite, Marsden, Greenfield and Mossley(Manchester).
- The stations were in reasonable condition, but some needed new footbridges and a bit of refurbishment.
- There was virtually no signs of any foundations for electrification.
This map shows the route.
Note.
- The pink tracks are the Manchester Metrolink.
- The red tracks are electrified at 25 KVAC overhead.
- The red and black tracks are being electrified.
- Huddersfield is indicated by the blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map.
- Stalybridge station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The pink track in the South-West corner of the map is the Manchester Metrolink branch to Ashton-under-Lyme.
- The route between Huddersfield and Stalybridge is shown as it will will be fully electrified.
- Huddersfield and Stalybridge is 18 miles.
- There are three short tunnels between Huddersfield and Stalybridge.
I wonder, if it would be more affordable to not put up wires between Huddersfield and Stalybridge and use battery-electric passenger trains and hydrogen freight locomotives?
Stalybridge Station
I took these pictures at Stalybridge station.
The station is fully-electrified and has direct services to Huddersfield, Hull, Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester Piccadilly, Manchester Victoria, Newcastlle, Wigan and York.
Will Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle Be Fully Electrified?
Consider.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Newcastle stations is 180.8 miles.
- Newcastle and Church Fenton stations is 91.4 miles and is fully-electrified.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Stalybridge stations is 39.4 miles and is fully-electrified.
This means that the gap between Church Fenton and Stalybridge stations is just fifty miles.
Real Time Trains indicate that the current Class 802 trains on the route run on diesel between Stalybridge and York stations, which is 60.8 miles.
- Changing power in Stalybridge and York stations means if anything goes wrong passengers can be easily rescued.
- From what I saw on Thursday, it looks like electrification will be completed between Neville Hill depot and Huddersfield.
I wouldn’t be surprised, if they just electrified to the West of Stalybridge and the East of Huddersfield.
That would mean that the 18 miles between Stalybridge and Huddersfield would be run on batteries.
- But it would also avoid electrifying three tunnels.
- How much disruption would be saved, by not electrifying the tunnels?
- Freight trains would use something like a bi-mode Class 99 locomotive, but it would only need a range of 18 miles on diesel.
I can also see improvised bi-mode locomotives being used like this combination of a Class 66 and Class 90 locomotives.
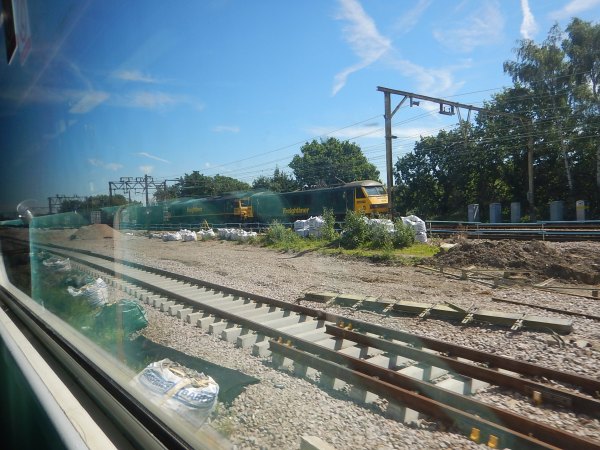

It was certainly doing its job, when I saw the combination at Shenfield.
The Problem Of Electrifying Leicester Station
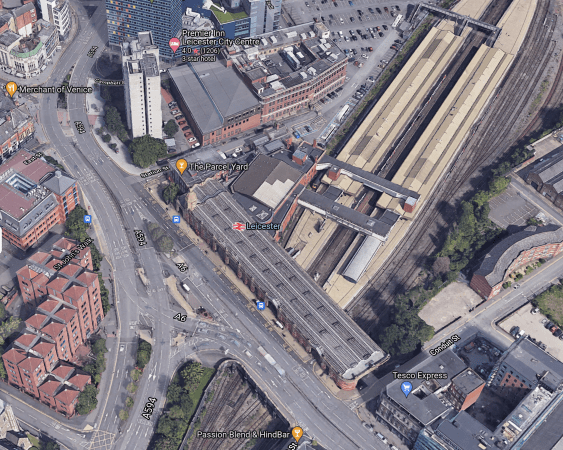
This post is my attempt to try and explain the problem of electrifying the Midland Main Line through Leicester station.
This Google map shows the Southern end of the station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the station.
Note.
- There appear to be five tunnels under the station buildings and London Road.
- What is the tunnel going underneath the tracks used for?
Leicester station has a Grade II Listed frontage.
Note.
- It is an impressive Victorian station.
- The station building is on a bridge over the tracks.
- The station is also on one of the main roads through Leicester.
- The road layout is very complicated.
This 3D Google Map, shows an aerial view of the station.
Note.
- There four platforms, which are numbered 1-4 from the left.
- The expresses between London and Derby, Nottingham and Sheffield use the two middle tracks.
- Other main line and East-West services use the outside platforms.
- There is an avoiding line for freight services.
- 5. The step-free footbridge is clearly visible.
This second 3D Google Map, shows an enlargement of the frontage of the station.
These pictures show what is inside the building at the front of the station.
The building would appear to be a Grade II Listed taxi rank and free twenty-minute car park.
There are plans to increase the capacity of the station.
- A fifth platform will be added.
- Three miles of quadruple track will be be built South of the station.
- The Midland Main Line was also to be electrified.
Real Time Trains indicates that the distance between Leicester and Wigston North junction is 3.1 miles.
This OpenRailMap shows that section of track.
Note.
- Leiester station is at the top of the map.
- Wigston junction is the triangular junction at the bottom of the map.
- Wigston North Junction is indicated by the blue arrow.
- OpenRailwayMap only shows a 100 mph Northbound track and a 90 mph Southbound track on the route.
It looks to me, that four tracks between Leicester and Wigston North junction would mean that trains could expedite arrivals to and departures from Leicester to and from the South.
South From Wigston Junction
Consider.
- London St. Pancras and Kettering is a four-track railway as far as the Corby Branch.
- North of Luton the slowest maximum speed is 100 mph, with much of the line rated at 110 mph plus.
- Wigston North junction and Luton station is 65.8 miles.
- Current Class 222 diesel trains typically take 40 minutes.
- This is an average speed of 98.7 mph.
- An average speed of 110 mph between Wigston North junction and Luton station would take 36 minutes.
- An average speed of 125 mph between Wigston North junction and Luton station would take 31.6 minutes.
- An average speed of 130 mph between Wigston North junction and Luton station would take 30.4 minutes.
I believe with track improvements and digital signalling, there are time savings to be gained between St. Pancras and Leicester stations.
Ultimately, if the 140 mph design speed of the Class 810 trains under digital signalling could be maintained, this would do the following.
- Push the St. Pancras and Leicester times under an hour.
- Push the St. Pancras and Nottingham times under ninety minutes.
- Push the St. Pancras and Sheffield times under two hours.
Batteries would only be used on the three miles between Wigston North junction and Leicester station.
Could Bi-Mode Trains Be Used?
They could be used initially and to prove if the partial electrification works.
But each train has four diesel engines and sometimes they will be working in pairs through the stations between Leicester and Sheffield.
Passengers will take a dim view of being covered in lots of diesel smoke, when they have been promised clean, zero-carbon electric trains.
But the battery-electric trains will be much quieter and pollution-free.
This page on the Hitachi Rail web site is entitled Intercity Battery Trains.
New Infrastructure Needed
The only infrastructure needed will be that which will support the new trains.
The Class 810 trains will be maintained at Etches Park at Derby.
If they are battery-electric trains, there may be some strategically-placed chargers, which typically would be a short length of overhead wire.
Government Pauses Midland Main Line Electrification
This is the first paragraph of this article on Modern Railways.
The Government has paused the third phase of Midland main line electrification to Sheffield and Nottingham, plus the final phase of the South West Rail Resilience Programme (SWRRP), which involves strengthening cliffs at Holcombe.
Currently, the Midland Main Line electrification appears to have been installed between London St. Pancras and Wigston, where there is a triangular junction.
This article on Modern Railways is entitled MML Wires To Wigston energised, says this in the first paragraph.
A major milestones on the Midland Main Line has been achieved with the energisation of the newly installed overhead wires between Kettering and Wigston and the first trip for a new East Midlands Railway Aurora bi-mode unit to St Pancras.
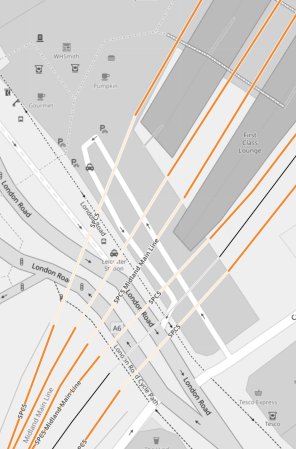
This OpenRailwayMap shows the Midland Main Line between Leicester station and Wigston junction.
Note.
- Red tracks are electrified.
- Black tracks are not electrified.
- Black/red dashed tracked are being electrified.
- Wigston junction is at the bottom of the map.
- The red track indicates that the South of the junction is electrified.
- The North of the junction is now electrified according to the Modern Railways article.
- The West of the junction is not electrified and leads to the electrified Trent Valley Line at Nuneaton.
- The junction in the middle of the map is Knighton junction, that leads to Burton-on-Trent station.
- In the North-East corner of the map is Leicester station.
Distances from the electrified part of Wigston junction are as follows.
- Derby – 32.5 miles
- Leeds – 107.8 miles
- Leicester – 13.1 miles
- Nottingham – 30.5 miles
- Nuneaton – 15.6 miles
- Sheffield – 68.9 miles
I asked Google AI how far one of Hitachi’s Class 802 trains had gone during tests and got this reply.
A Class 802 train, when operating solely on battery power, can achieve a range of approximately 44 miles (70 km). This was demonstrated in a trial where a five-car Class 802/2 train reached a maximum speed of 87 mph using battery power alone, covering non-electrified sections. Hitachi Rail and Angel Trains are conducting trials to assess the viability of battery technology for longer distances and to reduce reliance on diesel power on non-electrified sections of routes.
Hitachi’s tests were performed with just one diesel engine replaced by a battery pack and it should be born in mind, that the Class 810 trains, that will be used on the Midland Main Line have four diesel engines.
As an electrical engineer, I feel battery range should be additive, so a three-battery train could have a range as much as 120 miles.
- This range would do nicely for a London and Leeds service, as Leeds station is fully-electrified to charge a train for return.
- As London and Sheffield return would be 137.8 miles, a charge at Sheffield would probably be needed to top-up the batteries.
On the other hand a two-battery and two-diesel unit, would have a battery range sufficient for the following services.
- London and Derby and return.
- London and Nottingham and return.
- London and Sheffield with return after a charge.
- London and Leeds with an intermediate charge at Sheffield.
We live in very electrifying times.
I am sure, that Hitachi and their battery-makers will find a solution to run all-electric services to the North of Wigston junction, without full electrification, but with just a charger at Sheffield.
The Electrification Problem At Leicester
Some years ago I came back to London from Leicester with a group of drivers. At one point, the conversation turned to electrification and they said that they had met a Network Rail engineer, who had told them, that the bridge was rather low for electrification and the track couldn’t be lowered because Leicester’s main sewer was underneath the railway.
In Leicester Station – 4th Jan 2022, I show a selection of pictures of Leicester station’s Grade II Listed frontage.
I doubt it would be possible to seriously alter Leicester station to electrify it, as the Heritage Taliban would have a field day.
But if I’m right that all services will be run North of Wigston on batteries, there will be no need to electrify through Leicester station.
Not only would using batter-electric trains probably be more affordable than electrification, but also because of the Leicester problem, it would be less inconvenient for passengers.
Could London and Leicester Be Run In An Hour Or Even Less?
Consider.
- The London and Sheffield services, which go non-stop between London and Leicester take around 64-66 minutes.
- The London and Nottingham services, which stop at Market Harborough take about 5-6 minutes longer.
- London and Leicester is 98.9 miles.
- The fastest trains average 93 mph between London and Leicester.
- Much of the route between London and Leicester has a maximum speed of 100 mph or more, with some sections of 125 mph running.
- Regenerative braking should reduce the time for the Market Harborough stop.
I can certainly see the non-stop Sheffield services being timed at under an hour between London and Leicester.
But I wouldn’t rule out all services between London and Leicester being timed at under an hour.
Could London and Sheffield Be Run In Two Hours Or Even Less?
Given that most services between London and Sheffield take two hours and four minutes and I reckon six minutes could be saved between London and Leicester, I suspect two hours or less is a very attainable target for London and Sheffield services.
Why Not Fit Four Batteries And Be Done With it?
I suspect it will be down to reliability and whether running the diesels on hydrotreated vegeatble oil is acceptable to some politicians.
Would This Be The World’s First Battery-Electric Main Line With 200 kph Running?
Quite possibly!
Conclusion
I can see no disadvantage in not electrifying North of Wigston junction and using battery-electric trains.
It could even be a lot more affordable.
Dore & Totley Station – 1st April 2025
It seems like only yesterday, when I visisited Dore and Totley station and wrote Dore And Totley Station – 13th July 2020, when I took these pictures.
But it was yesterday, when I visited the station again and look at the station now.
Note.
- The footbridge is in keeping with the original station building.
- The only changes to the original station building, is a small amount of tasteful restoration.
- The footbridge is high enough for future electrification.
- There are one shelter on the entry/car park and two on the far side.
- As I watched several Class 158, Class 195 and Class 222 trains pass through, it appears that the curve has been profiled for speed.
- I am pretty sure, that the station has been designed so that if required, at least one extra platform can be added to the Chesterfield Lines.
- The Rajdhani Restaurant in the original station building is rated 4.2 on Trip Advisor, which says they do gluten-free options.
- The maximum speed through the station appears to be 50 mph, with 70 mph on the Chesterfield Lines.
From my brief visit, it appears to be another station, that has been superbly updates.
Let’s bring on a few more.
The Train Trip Where I Arrived Before My Train
Yesterday, I went to Sheffield on Grand Central Trains. But owing to a small mix-up at Peterborough station, I ended up getting to Doncaster on an LNER train, before my Grand Central Train arrived.
This was the sequence of events.
- I bought a ticket from a machine at King’s Cross for Doncaster for the keen single price of £25.70 with my Senior Railcard.
- I had managed to assign myself a forward facing window seat.
- The aisle seat was occupied by a large man before I took my seat.
- But I was able to squeeze past.
- I did tell my travelling companion that I was going to Doncaster., as I have been known to fall asleep on trains and didn’t want to end up in Bradford.
- My train left for Doncaster at 10:52.
- I then found thyself waking up, with the train stopped in a station, which I didn’t recognise.
- So I asked my companion, where we were and he said. “Doncaster!”
- I then squeezed past him again and left the train, only to find, that I had got out at Peterborough.
- Luckily, by the time I realised I was at the wrong station, an LNER train had arrived that was also going to Doncaster.
- So a helpful member of LNER’s station staff told me to get on the LNER train.
- Another helpful member of LNER’s train staff approved my ticket, so I didn’t have to buy another.
- As my new train, passed Retford, we passed the Grand Central Train at rest in Retford station.
- I arrived in Doncaster at 12:45.
Looking at Real Time Trains, I find this is said.
This service was cancelled between Retford and Bradford Interchange due to the train striking a bird (V8)
As it was a V8 bird, I assume it was a large one.
New Cut-Price Sheffield to London King’s Cross Train Service A Step Closer After Breakthrough
The title of this post, is the same as that of a story on The Star.
This is the sub-heading.
A new cut-price Sheffield to London train service has moved a step closer after a significant breakthrough.
These two paragraphs add detail to the story.
Hull Trains, which is part of FirstGroup, wants to launch a twice-daily return service between Sheffield and London King’s Cross, via Woodhouse, Worksop and Retford.
It says fares would be up to 30 per cent cheaper and the new route would provide more choice for passengers, especially for students and other people on a tighter budget.
I would assume the breakthrough is that the new East Coast Main Line timetable has been agreed.
The article confirms this.
The new East Coast Mainline timetable coming into operation later this year has been confirmed by Network Rail, making it easier to see how the new Sheffield-London trains would fit in around existing services.
Ever since I saw this proposed service, I wondered if by judicious splitting and joining at Retford, the Hull Trains services would effectively be only one ten car train on the East Coast Main Line.