Cummins To Cease New Electrolyser Activity Amid Worsening Market
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Renewables Now.
These are the first three paragraphs.
Cummins Inc has decided to stop new commercial activity in the electrolysers space following a strategic review of the segment launched last year, citing deteriorating market conditions and weakening customer demand.
The decision is linked to USD 458 million (EUR 388.4m) of charges for the full-year 2025 related to the electrolyser business within the company’s zero-emission technologies arm, Accelera, of which USD 415 million were non-cash charges.
The company noted that it will continue to fulfil existing customer commitments before winding down new commercial activity in the segment.
Although, I am in favour of using hydrogen as a fuel, I recognise, that traditional electrolysis is not the most efficient process.
These methods are more efficient.
HiiROC
- HiiROC use a process, that they call Thermal Plasma Electrolysis to split any hydrocarbon gas into hydrogen and carbon black.
- HiiROC originated in the University of Hull.
- Typical gases that can be used are chemical plant off-gas, biomethane and methane.
- I like the ability to use chemical plant off-gas, as some of this is particularly nasty and HiiROC may offer safe disposal.
But the big advantage is that the HiiROC process is five times more energy efficient than traditional electrolysis.
The carbon black is no useless by-product, but has several valuable uses in its own right, which are detailed in its Wikipedia entry.
These two paragraphs from Wikipedia, give a summary of the more common uses of carbon black.
The most common use (70%) of carbon black is as a reinforcing phase in automobile tires. Carbon black also helps conduct heat away from the tread and belt area of the tire, reducing thermal damage and increasing tire life. Its low cost makes it a common addition to cathodes and anodes and is considered a safe replacement to lithium metal in lithium-ion batteries. About 20% of world production goes into belts, hoses, and other non-tire rubber goods. The remaining 10% use of carbon black comes from pigment in inks, coatings, and plastics, as well as being used as a conductive additive in lithium-ion batteries.
Carbon black is added to polypropylene because it absorbs ultraviolet radiation, which otherwise causes the material to degrade. Carbon black particles are also employed in some radar absorbent materials, in photocopier and laser printer toner, and in other inks and paints. The high tinting strength and stability of carbon black has also provided use in coloring of resins and films. Carbon black has been used in various applications for electronics. A good conductor of electricity, carbon black is used as a filler mixed in plastics, elastomer, films, adhesives, and paints. It is used as an antistatic additive agent in automobile fuel caps and pipes.
It can also be used as a soil improver in agriculture.
HiiROC would appear to be five times more energy efficient than traditional electrolysis.
I would also rate the range of their investors as a particular strength.
Google AI lists these companies as investors.
HiiROC, a UK-based developer of plasma torch technology for “turquoise” hydrogen production, is backed by a consortium of industrial and strategic investors. Key investors include Centrica, Melrose Industries, Hyundai Motor Company, Kia, HydrogenOne Capital, CEMEX Ventures, Wintershall Dea, and VNG.
Note.
- CEMEX must be going to decarbonise cement making.
- Melrose describe themselves as an industry-leading aerospace technology provider.
- Will we be seeing hydrogen cars from Korean manufacturers?
- Wintershall Dea is Europe’s leading independent gas and oil company.
HiiROC has an impressive list of investors.
Bloom Energy
I wrote about Bloom Energy’s process in Westinghouse And Bloom Energy To Team Up For Pink Hydrogen.
This method also looks promising.
- Westinghouse Electric Company is an American builder of nuclear power stations.
- Bloom Energy Corporation make a solid-oxide electrolyser.
- Pink hydrogen is green hydrogen produced using nuclear power.
It uses electrolysis at a higher temperature, which speeds it up.
Desert Bloom
This is an Australian process, that I wrote about in 10GW Green Hydrogen Project Aims To Electrolyze Water Drawn From Desert Air.
Conclusion
You can understand, why Cummins are getting jumpy!
But you have to remember that when I worked in a hydrogen plant in the 1960s, the hydrogen was an unwanted by-product and it was mixed with coal gas and sent down the power station to raise steam, so that it could be used to do something useful.
Centrica And X-energy Agree To Deploy UK’s First Advanced Modular Reactors
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica and X-Energy, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of X-Energy Reactor Company, LLC, today announced their entry into a Joint Development Agreement (JDA) to deploy X-energy’s Xe-100 Advanced Modular Reactors (“AMR”) in the United Kingdom.
These three paragraphs add more details.
The companies have identified EDF and Centrica’s Hartlepool site as the preferred first site for a planned U.K. fleet of up to 6 gigawatts.
The agreement represents the first stage in a new trans-Atlantic alliance which could ultimately mobilise at least £40 billion in economic value to bring clean, safe and affordable power to thousands of homes and industries across the country and substantive work for the domestic and global supply chain.
A 12-unit Xe-100 deployment at Hartlepool could add up to 960 megawatts (“MW”) of new capacity, enough clean power for 1.5 million homes and over £12 billion in lifetime economic value. It would be developed at a site adjacent to Hartlepool’s existing nuclear power station which is currently scheduled to cease generating electricity in 2028. Following its decommissioning, new reactors would accelerate opportunities for the site and its skilled workforce. The site is already designated for new nuclear under the Government’s National Policy Statement and a new plant would also play a critical role in generating high-temperature heat that could support Teesside’s heavy industries.
This is no toe-in-the-water project, but a bold deployment of a fleet of small modular reactors to provide the power for the North-East of England for the foreseeable future.
These are my thoughts.
The Reactor Design
The Wikipedia entry for X-energy has a section called Reactor Design, where this is said.
The Xe-100 is a proposed pebble bed high-temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactor design that is planned to be smaller, simpler and safer when compared to conventional nuclear designs. Pebble bed high temperature gas-cooled reactors were first proposed in 1944. Each reactor is planned to generate 200 MWt and approximately 76 MWe. The fuel for the Xe-100 is a spherical fuel element, or pebble, that utilizes the tristructural isotropic (TRISO) particle nuclear fuel design, with high-assay LEU (HALEU) uranium fuel enriched to 20%, to allow for longer periods between refueling. X-energy claims that TRISO fuel will make nuclear meltdowns virtually impossible.
Note.
- It is not a conventional design.
- Each reactor is only about 76 MW.
- This fits with “12-unit Xe-100 deployment at Hartlepool could add up to 960 megawatts (“MW”) of new capacity” in the Centrica press release.
- The 960 MW proposed for Hartlepool is roughly twice the size of the Rolls-Rpoyce SMR, which is 470 MW .
- Safety seems to be at the forefront of the design.
- I would assume, that the modular nature of the design, makes expansion easier.
I have no reason to believe that it is not a well-designed reactor.
Will Hartlepool Be The First Site?
No!
This page on the X-energy web site, describes their site in Texas, which appears will be a 320 MW power station providing power for Dow’s large site.
There appear to be similarities between the Texas and Hartlepool sites.
- Both are supporting industry clustered close to the power station.
- Both power stations appear to be supplying heat as well as electricity, which is common practice on large industrial sites.
- Both use a fleet of small modular reactors.
But Hartlepool will use twelve reactors, as opposed to the four in Texas.
How Will The New Power Station Compare With The Current Hartlepool Nuclear Power Station?
Consider.
- The current Hartlepool nuclear power station has two units with a total capacity of 1,185 MW.
- The proposed Hartlepool nuclear power station will have twelve units with a total capacity of 960 MW.
- My instinct as a Control Engineer gives me the feeling, that more units means higher reliability.
- I suspect that offshore wind will make up the difference between the power output of the current and proposed power stations.
As the current Hartlepool nuclear power station is effectively being replaced with a slightly smaller station new station, if they get the project management right, it could be a painless exercise.
Will This Be The First Of Several Projects?
The press release has this paragraph.
Centrica will provide initial project capital for development with the goal of initiating full-scale activities in 2026. Subject to regulatory approval, the first electricity generation would be expected in the mid-2030s. Centrica and X-energy are already in discussions with additional potential equity partners, as well as leading global engineering and construction companies, with the goal of establishing a UK-based development company to develop this first and subsequent projects.
This approach is very similar to the approach being taken by Rolls-Royce for their small modular reactors.
Will Centrica Use An X-energy Fleet Of Advanced Modular Reactors At The Grain LNG Terminal?
This press release from Centrica is entitled Investment In Grain LNG Terminal.
This is one of the key highlights of the press release.
Opportunities for efficiencies to create additional near-term value, and future development options including a combined heat and power plant, bunkering, hydrogen and ammonia.
Note.
- Bunkering would be provided for ships powered by LNG, hydrogen or ammonia.
- Heat would be needed from the combined heat and power plant to gasify the LNG.
- Power would be needed from the combined heat and power plant to generate the hydrogen and ammonia and compress and/or liquify gases.
Currently, the heat and power is provided by the 1,275 MW Grain CHP gas-fired power station, but a new nuclear power station would help to decarbonise the terminal.
Replacement Of Heysham 1 Nuclear Power Station
Heysham 1 nuclear power station is part-owned by Centrica and EdF, as is Hartlepool nuclear power station.
Heysham 1 nuclear power station is a 3,000 MW nuclear power station, which is due to be decommissioned in 2028.
I don’t see why this power station can’t be replaced in the same manner as Hartlepool nuclear power station.
Replacement Of Heysham 2 Nuclear Power Station
Heysham 2 nuclear power station is part-owned by Centrica and EdF, as is Hartlepool nuclear power station.
Heysham 2 nuclear power station is a 3,100 MW nuclear power station, which is due to be decommissioned in 2030.
I don’t see why this power station can’t be replaced in the same manner as Hartlepool nuclear power station.
Replacement Of Torness Nuclear Power Station
Torness nuclear power station is part-owned by Centrica and EdF, as is Hartlepool nuclear power station.
Torness nuclear power station is a 1,290 MW nuclear power station, which is due to be decommissioned in 2030.
I don’t see why this power station can’t be replaced in the same manner as Hartlepool nuclear power station.
But the Scottish Nationalist Party may have other ideas?
What Would Be The Size Of Centrica’s And X-energy’s Fleet Of Advanced Modular Reactors?
Suppose.
- Hartlepool, Grain CHP and Torness power stations were to be replaced by identical 960 MW ADRs.
- Heysham 1 and Heysham 2 power stations were to be replaced by identical 1,500 MW ADRs.
This would give a total fleet size of 5,880 MW.
A paragraph in Centrica’s press release says this.
The companies have identified EDF and Centrica’s Hartlepool site as the preferred first site for a planned U.K. fleet of up to 6 gigawatts.
This fleet is only 120 MW short.
Centrica Secures Investment Stake In Gasrec Helping Boost UK Bio-LNG Ambitions
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica has secured a minority stake in Gasrec, the UK’s largest dual provider of bio-LNG (bio-Liquified Natural Gas) and bio-CNG (bio-Compressed Natural Gas) to the road transport sector,
These first two paragraphs give more details.
Gasrec says the investment will drive the next phase of its infrastructure ambitions, with plans to open a UK wide network of open-access refuelling stations supplying renewable bio-LNG for the decarbonisation of heavy goods vehicles.
Centrica is taking a 16% stake and becomes one of three major shareholders in Gasrec, alongside global integrated energy company bp and private family office 44 North.
I have some thoughts.
Does Running A Truck On bio-LNG or bio-CNG. Reduce Carbon Emissions?
This paragraph from the press release, gives the thoughts of Chris O’Shea, who is Group Chief Executive, Centrica.
Chris O’Shea, Group Chief Executive, Centrica plc, said: “Demand for bio-LNG for transport is growing fast as more HGV operators make the switch – drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel*. This investment in Gasrec enhances our collaboration with the leading company in the sector, and puts us in a strong position to energise a vital sector of the industry on its journey to net zero.”
As Centrica is a public company, with shareholders, who would take a dim view of Mr. O’Shea telling porkies, I suspect we can assume that the following is true.
Drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel.
The asterisk in the full quote, refers to this note.
Low Carbon Vehicle Partnership, Innovate UK and Office for Low Emission Vehicles, Low Emission Freight & Logistics Trial (LEFT), Key Findings, November 2020. Using specific feedstocks CO2 reductions of 200% are achievable.
Centrica could be being conservative with their claims.
Decarbonising Buses, Locomotives And Trucks
Despite what Elon Musk, would have us believe, electric trucks will not dominate the future of freight transport.
An electric truck would be the vehicle equivalent of asking Usain Bolt to run a hundred metres with a large refrigerator on his back.
Trucks are going to need a fuel without a weight penalty and with a long range.
I asked Google for information about Cummins diesel, natural gas and hydrogen engines and received this AI Overview.
Cummins offers engines powered by diesel, natural gas, and hydrogen. While diesel engines are well-established, Cummins is also developing both natural gas and hydrogen engines, particularly focusing on hydrogen as a pathway to zero-carbon solutions for various applications. Cummins utilizes a fuel-agnostic platform, meaning a common base engine can be adapted for different fuel types, including diesel, natural gas, and hydrogen.
Recently, GB Railfreight purchased thirty Class 99 locomotives from Stadler.
- They can use electrification, where it exists.
- Where electrification doesn’t exist, they can use an onboard Cummins diesel engine, which is built in Darlington.
- In electric-mode, they have 6.2 MW of power, and are the most powerful locomotives ever to run on UK railways.
- In diesel-mode, they have 1.8 MW of power, which is more than enough to haul a large container train in and out of Felixstowe.
I had thought that at some future date, Cummins would convert these locomotives to electro-hydrogen.
But now that Gasrec is providing bio-LNG and bio-CNG, GB Railfreight, have the option of converting both hydrogen and biomethane.
Similar logic can be applied to Wrightbus’s Streetdeck Ultroliner, one version of which is fitted with a Cummins engine, that can be converted to electric, hydrogen or natural gas, which of course includes biomethane. This page on the Wrightbus web site describes the bus.
Wrightbus are also going back into coach manufacture, as I wrote about in Wrightbus Goes Back To The Future As It Relaunches The Contour Coach. As with the Streetdeck Ultroliner, Cummins seem to be providing one of the power units.
It seems to me, that the zero- and low-carbon revolution in transport will generate a need for the availability of biomethane, hydrogen and natural gas fuel for transport all over the country.
Gasrec with around twenty biomethane fuelling points around the country, seem well-placed to supply the biomethane in bio-LNG or bio-CNG form.
Could Gasrec Deliver Hydrogen?
Various bus companies in the UK, have had difficulty getting the fuel for their hydrogen buses.
I believe that delivering hydrogen would be very similar to delivering LNG and if Gasrec can deliver LNG successfully and safely, they probably have the technology to do the same for hydrogen.
Centrica Seem To Be Assembling An Interesting Consortium
These are some deals, that I have reported on this blog, that involve Centrica.
- Centrica, along with Hyundai, Kia, Siemens and others have backed Hull-based hydrogen start-up; HiiROC, who can produce affordable hydrogen from any hydrocarbon gas including natural gas, where it is needed.
- Centrica have invested in Sizewell C. Will they be using their share of the electricity to make affordable pink hydrogen using HiiROC?
- In Centrica And Ryze Agree To Develop Hydrogen Pathway, I talked about how Centrica and Ryse were aiming to bring hydrogen to the masses.
- In Recurrent Energy’s Middle Road Project Sold To Centrica, I talked about a Centrica investment in solar power.
- In Aberdeen’s Exceed Secures Centrica Rough Contract, I talked about how Centrica were redeveloping the Rough gas storage site for hydrogen.
- In Lhyfe And Centrica To Develop Offshore Renewable Green Hydrogen In The UK, I talked about developing offshore hydrogen.
- In Centrica Announces Hydrogen Ready Combined Heat And Power Partnership With 2G, the title says it all.
- In Centrica Signs UK Biomethane Agreement With Yorkshire Water And SGN Commercial Services, Centrica appear to be sourcing biomethane from Yorkshire Water.
- In Centrica Invests In Renewable Energy Storage Capabilities To Boost UK’s Energy Security And Accelerate Transition To Net Zero, I talk about Centrica, Goldman Sachs and others, investment in liquid-air energy storage company; Highview Power.
- In British Gas Owner Mulls Mini-Nuke Challenge To Rolls-Royce, I talk about rumours that Centrica might invest in SMRs.
Note.
- A lot of these deals are are about hydrogen production.
- Some of these deals are about biomethane production.
- None of these deals talk about getting hydrogen and biomethane to customers.
It appears to me, that Gasrec have a model that works to get hydrogen, methane and biomethane from production and storage to the end customers.
Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network
In Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network, I talked about supplying all those millions of off-gas grid properties with hydrogen for heating, agricultural and industrial purposes, in the countryside of the UK.
Gasrec have the technology to decarbonise the countryside.
Conclusion
Gasrec would appear to be a very useful partner for Centrica.
Hydrogen Deployment Milestone For Cemex And HiiROC
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Agg-Net.
This is the sub-heading.
Cemex kick-start first-of-a-kind low-carbon hydrogen project using thermal plasma electrolysis in cement production
These first two paragraphs add more detail.
CEMEX Ventures, Cemex’s corporate venture capital (CVC) and open innovation unit, announced today an initial hydrogen deployment at industrial scale with HiiROC, the pioneering British hydrogen company that produces affordable, clean hydrogen, at their Rugby cement plant in the UK.
Hydrogen has emerged as a low-carbon energy source within the construction industry’s decarbonization roadmap and offers potential as an energy solution to help reduce the sector’s reliance on fossil fuels and lower CO2 emissions. This venture marks a significant milestone for Cemex, as it represents the beginning of a large-scale strategic project plan with the aim to further lower their carbon emissions in cement production.
These third paragraph is a good outline of HiiROC and how it can be deployed.
HiiROC produce carbon-neutral hydrogen using their proprietary Thermal Plasma Electrolysis (TPE) process, which requires just one-fifth of the electrical energy used in water electrolysis and captures carbon as a solid by-product, avoiding CO2 emissions – a game-changer for the industry. HiiROC’s modular solution can be deployed as single units to full-scale industrial plants, and the hydrogen produced can be used as an alternative energy source to fuel clinker production processes, helping Cemex to achieve their decarbonization goals.
Centrica, Cemex, Hyundai, Kia and others are investors in HiiROC.
I asked Google AI, what percentage of carbon emissions came from cement production and got this answer.
Cement production accounts for roughly 8% of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, according to think tank Chatham House. This makes it a significant contributor to climate change, with the industry’s emissions comparable to the total emissions of some countries.
If HiiROC can take a big bite out of carbon emissions, by reducing cement production’s 8 % share, they would be on a winner.
Centrica Really Can’t Lose At Sizewell
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica’s £1.3 billion investment in Sizewell C guarantees substantial returns, even with cost overruns.
These two-and-a-half paragraphs explain the funding.
Now we know what Ed Miliband means by his “golden age of nuclear” — golden for the companies putting their money into Sizewell C. Yes, reactor projects have a habit of blowing up private investors. But maybe not this one. It looks more like an exercise in transferring risk to consumers and the taxpayer.
Sure, nobody builds a £38 billion nuke on a Suffolk flood plain without a frisson of danger. But the energy secretary and his Treasury chums have done their bit to make things as safe as possible for the companies putting in equity alongside the government’s 44.9 per cent stake: Canada’s La Caisse with 20 per cent, British Gas-owner Centrica (15 per cent), France’s EDF (12.5 per cent) and Amber Infrastructure (7.6 per cent).
For starters, nearly all the debt for the 3.2 gigawatt plant, three-quarters funded by loans, is coming from the state-backed National Wealth Fund. It’s bunging in up to £36.6 billion, with £5 billion more guaranteed by a French export credit agency.
It looks to me that between them the British and French governments are providing £41.5 billion of loans to build the £38 billion nuke.
These are my thoughts.
Hydrogen And Sizewell C
This page on the Sizewell C web site is entitled Hydrogen And Sizewell C.
Under a heading of Hydrogen Buses, this is said.
At Sizewell C, we are exploring how we can produce and use hydrogen in several ways. We are working with Wrightbus on a pilot scheme which, if successful, could see thousands of workers transported to and from site on hydrogen double decker buses. You can read more about the pilot scheme in our press release
Firstly, it could help lower emissions during construction of the power station. Secondly, once Sizewell C is operational, we hope to use some of the heat it generates (alongside electricity) to make hydrogen more efficiently.
This would appear to be a more general statement about hydrogen and that the following is planned.
- Hydrogen-powered buses will be used to bring workers to the site. A press release on the Sizewell C web site, talks about up to 150 buses. That would probably be enough buses for all of Suffolk.
- Hydrogen-powered construction equipment will be used in the building of the power station.
- It also talks about using the excess heat from the power station to make hydrogen more efficiently. I talk about this process in Westinghouse And Bloom Energy To Team Up For Pink Hydrogen.
This is a substantial investment in hydrogen.
Centrica And Electricity From Sizewell C
The article in The Times, also says this.
Even so, there’s a fair bit of protection for the likes of Centrica, which has also agreed a 20-year offtake deal for its share of Sizewell’s electricity. The price of that is not yet known.
Nothing is said in the article about the size of Centrica’s electricity offtake.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell C, that would by 480 MW.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell B + C, that would by 660 MW.
If they use their share to generate hydrogen, Suffolk would have a massive hydrogen hub.
To power the buses and construction of Sizewell C, Sizewell B could be used to provide electricity to create the hydrogen.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Produced?
Centrica, along with other companies, who include Hyundai and Kia, are backers of a company in Hull called HiiROC, who use a process called Thermal Plasma Electrolysis to generate hydrogen.
On their web site, they have this sub-heading.
A Transformational New Process For Affordable Clean Hydrogen
The web site also describes the process as scalable from small modular units up to industrial scale. It also says this about the costs of the system: As cheap as SMR without needing CCUS; a fraction of the energy/cost of water electrolysis.
If HiiROC have achieved their objective of scalability, then Centrica could grow their electrolyser to meet demand.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Distributed?
Consider.
- Currently, the Sizewell site has both road and rail access.
- I can still see in my mind from the 1960s, ICI’s specialist articulated Foden trucks lined up in the yard at Runcorn, taking on their cargoes of hydrogen for delivery all over the country.
- As that factory is still producing hydrogen and I can’t remember any accidents in the last sixty years, I am fairly sure that a range of suitable hydrogen trucks could be developed to deliver hydrogen by road.
- The road network to the Siewell site is being updated to ensure smooth delivery of workers and materials.
- The rail access to the Sizewell site is also being improved, for the delivery of bulk materials.
I believe there will be no problems delivering hydrogen from the Sizewell site.
I also believe that there could be scope for a special-purpose self-propelled hydrogen tanker train, which could both distribute and supply the hydrogen to the vehicles, locomotives and equipment that will be using it.
Where Will The Hydrogen Be Used?
I have lived a large part of my life in Suffolk and know the county well.
In my childhood, there was quite a lot of heavy industry, but now that has all gone and employment is based on agriculture, the Port of Felixstowe and service industries.
I can see hydrogen being used in the following industries.
Transport
Buses and heavy trucks would be powered by hydrogen.
The ports in the East of England support a large number of heavy trucks.
Large Construction Projects
Sizewell C is not the only large construction project in the East of England, that is aiming to use low-carbon construction involving hydrogen. In Gallagher Group Host Hydrogen Fuel Trial At Hermitage Quarry, I talked about a hydrogen fuel trial for the Lower Thames Crossing, that involved JCB and Ryse Hydrogen.
Hydrogen for the Lower Thames Crossing could be delivered from Sizewell by truck, down the A12.
Rail
We may not ever see hydrogen-powered passenger trains in this country, but I do believe that we could see hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
Consider.
- The latest electro-diesel Class 99 locomotives from Stadler have a Cummins diesel engine.
- The diesel engine is used, when there is no electrification.
- Cummins have developed the technology, that allows them to convert their latest diesel engines to hydrogen or natural gas power, by changing the cylinder head and the fuel system.
- Access to the Port of Felixstowe and London Gateway needs a locomotive with a self-powered capability for the last few miles of the route.
A Class 99 locomotive converted to hydrogen would be able to run with out emitting any carbon dioxide from Felixstowe or London Gateway to Glasgow or Edinburgh.
Ports
Ports have three main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for port workers.
- To fuel ships of all sizes from the humblest work-boat to the largest container ships.
- There may need to be fuel for hydrogen-powered rail locomotives in the future.
There are seven ports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth, Harwich, Ipswich, London Gateway, Lowestoft and Tilbury.
The proposed Freeport East is also developing their own green hydrogen hub, which is described on this page on the Freeport East web site.
Airports
Airports have two main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for airport workers.
- In the future, there is likely to be hydrogen-powered aircraft.
There are three airports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Norwich, Southend and Stansted.
Agriculture And The Rural Economy
Agriculture and the rural economy would be difficult to decarbonise.
Consider.
- Currently, most farms would use diesel power for tractors and agricultural equipment, which is delivered by truck.
- Many rural properties are heated by propane or fuel oil, which is delivered by truck.
- Some high-energy rural businesses like blacksmiths rely on propane, which is delivered by truck.
- Electrification could be possible for some applications, but ploughing the heavy land of Suffolk, with the added weight of a battery on the tractor, would probably be a mathematical impossibility.
- JCB are developing hydrogen-powered construction equipment and already make tractors.
- Hydrogen could be delivered by truck to farms and rural properties.
- Many boilers can be converted from propoane to run on hydrogen.
I feel, that hydrogen could be the ideal fuel to decarbonise agriculture and the rural economy.
I cover this application in detail in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Exports
Consider.
- Sizewell B and Sizewell C nuclear powerstations have a combined output of 4.4 GW.
- A rough calculation shows that there is a total of 7.2 GW of wind farms planned off the Suffolk coast.
- The East Anglian Array wind farm alone is said in Wikipedia to be planned to expand to 7.2 GW.
- The Sizewell site has a high capacity connection to the National Grid.
Nuclear plus wind should keep the lights on in the East of England.
Any excess electricity could be converted into hydrogen.
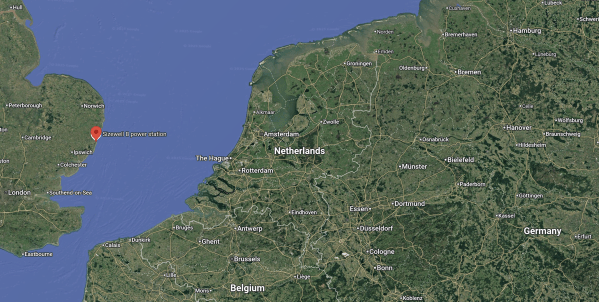
This Google Map shows the location of Sizewell B in relation to Belgium, Germany and The Netherlands.
The Sizewell site is indicated by the red arrow.
The offshore oil and gas industry has used technology like single buoy moorings and coastal tankers to collect offshore natural gas for decades.
I don’t see why coastal hydrogen tankers couldn’t export excess hydrogen to places around the North Sea, who need the fuel.
It should be born in mind, that Centrica have a good reputation in doing natural gas trading. This expertise would surely be useful in hydrogen trading.
Conclusion
I believe that a hydrogen hub developed at Sizewell makes sense and I also believe that Centrica have the skills and technology to make it work.
The British Mini Nuclear Fusion Reactor That Actually Works
The title of this post, is the same as that as this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
The only functional model in the world is so small it fits on a table and is set to help diagnose and cure cancer
These are the first two paragraphs, which add more details.
There are a few things that mark this nuclear fusion reactor out as unusual. For one, it is rather small: it could fit on a table top. For another, this research model currently has a little more gaffer tape than you might expect of the energy technology of the future.
But the biggest difference between it and its competitors is that this nuclear fusion reactor, in a warehouse north of Bristol, is actually working. And it is on the cusp of doing something more unusual still: making money.
It almost makes you think, that it should be filed under Too Good To Be True!
In the late 1960s, I shared an office at ICI Mond Division in Runcorn, with a guy, who was working on a process to make acetylene by a revolutionary route.
The process never worked, but now it has turned up being used by a company called HiiROC to make hydrogen.
They are also backed by some big names like Centrica, Hyundai, Kia and others.
I wonder how many other old ideas are finally ripe for developing, due to improvements in manufacturing and systems to control them.
South Korea Aims To Lead The Global Market With Hydrogen Train
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railly News.
These are the first two introductory paragraphs.
South Korea is taking an ambitious step with a vision of becoming a major player in the rapidly growing global hydrogen rail market. To 26,4 billion dollars The country that wants to gain a competitive advantage in this market that is expected to reach A self-developed Hydrogen Train by 2028 announced plans to introduce.
This strategic project is the national railway operator of South Korea korail will be managed by Korail, Building a two-car hydrogen train prototype by 2027 and creating the necessary legal and operational infrastructure for the dissemination of this technology. $23 million will make an investment. South Korean officials also clearly state that they aim to set international standards in the field of hydrogen-based mobility with this project.
I’ve thought for some time, that the Koreans have been serious about hydrogen-powered transport, as Hyundai keeps popping up with hydrogen transport and other ideas.
British company; Centrica owns a big share with Hyundai, Kia and others of a British start-up company from Hull, called HiiROC.
This is the HiiROC web site.
HiiROC can take any hydocarbon gas and split it into green hydrogen and carbon black.
Green hydrogen is obviously useful and the carbon black can be used for making tyres for vehicles, anodes for lithium-ion batteries and in agriculture for soil improvement.
Waste off-gas from a chemical plant can be split into green hydrogen and carbon black.
Biomethane from a sewage plant can be split into hydrogen and carbon black. Could a sewage plant on an estate be used to create biomethane for cooking and feeding to the HiiROC plant? Yes!
Could green hydrogen produced on the estate be used to drive vehicles like cars, vans and ride-on-mowers. Yes! If the manufacturer of the vehicle allows it!
How convenient would it be to have Hydrogen-at-Home?
The Korean investment in HiiROC by Hyundai and Kia clearly fits with the philosophy expressed in the second paragraph of the article of creating the hydrogen infrastructure.
I believe that at some point in the future, you will be able to buy a HiiROC device, that gives you as much hydrogen as you need to power your car, truck, bus, tram or train. The Koreans have a track record of turning ideas like this into reality.
Hyundai Unveils Upgraded Xcient Hydrogen Fuel Cell Truck
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Automotive Powertrain International.
This is the sub-heading.
Hyundai Motor Company has unveiled the upgraded Xcient fuel cell class-8 heavy-duty truck, which features advanced hydrogen technologies and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) tailored for the North American market.
The article is worth a full read, as it shows how the largest American trucks, can be replaced with zero-carbon hydrogen fuel cell trucks.
This is the Hyundai Xcient truck web site.
British Gas Partners With Strata And Daikin To Launch Eco-Tech Low Bill Homes
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
British Gas is set to supercharge sustainable living across the UK with the launch of Low Carbon Homes – a ground-breaking pilot in partnership with Strata and heat pump manufacturer, Daikin.
These are the first four paragraphs, which fill out a bit of detail.
In anticipation of The Future Homes Standard, customers will move into new build homes which have been fitted with a full range of the latest low-carbon technology at no extra cost to the housebuilder or owner. The homes will be equipped with a 6-8 kWh Daikin air source heat pump, 4 kWh solar panels, 5 kWh battery storage, Hive electric vehicle charger and thermostat. These items will be integrated into Hive’s award-winning app, providing customers with one-stop visibility and control of their energy usage.
The first trial phase will launch at a Strata’s “Breathe” development site in Kiveton, Rotherham. As a thank you for participating in the pilot, British Gas is giving homeowners access to a fixed rate tailored British Gas tariff. Participants in the trial will also have access to a dedicated British Gas energy manager to help them optimise the technology and keep bills as low as possible, while still meeting their desired comfort levels.
Each home will be fitted with a Hive hub, which connects to the WIFI network and acts as the home’s operating system, integrating all the sustainable technology. The customers energy and heat schedules and budget will be optimised by the Hive Hub for further savings.
When the customer connects to Hive’s app they will be able to control and maximise efficiency by setting schedules and spending budgets and allowing the Hub to help them reduce their bills.
Note.
- As a Control Engineer, this to me is a good start.
- I suspect that a 6-8 kWh Daikin air source heat pump, 4 kWh solar panels and 5 kWh battery storage will keep the average house warm.
- I would expect that the three companies have optimised the ratios between the sizes of the components to give the best performance.
It is amazing to think that it was in the early seventies, that in the two sections, where I worked at ICI, engineers had just started controlling and optimising flows, pressures and temperatures in complex chemical plants.
If you’d asked any of us, when our houses heating systems would be as fully controlled, we’d have given twenty years at most.
What kept the world so long?
I have a few thoughts.
Could The Housing Have Gas For Cooking??
Yes! Centrica owns a big share with Hyundai, Kia and others of a start-up company called HiiROC.
- This is the HiiROC web site.
- HiiROC can take any hydocarbon gas and split it into green hydrogen and carbon black.
- Green hydrogen is obviously useful and the carbon black can be used for making tyres for vehicles, anodes for lithium-ion batteries and in agriculture for soil improvement.
- Waste off-gas from a chemical plant can be split into green hydrogen and carbon black.
- Biomethane from a sewage plant can be split into hydrogen and carbon black. Could a sewage plant on an estate be used to create biomethane for cooking and feeding to the HiiROC plant? Yes!
- Could green hydrogen produced on the estate be used to drive vehicles like cars, vans and ride-on-mowers. Yes! If the manufacturer of the vehicle allows it!
- How convenient would it be to have Hydrogen-at-Home?
How Much Does A British Gas Hive Save On My Energy Bill?
I asked Google and I got this answer from Home Hive.
£119. A smaller carbon footprint and a smaller bill – our award-winning smart thermostat could cut your energy bills by up to £170 a year. Join Hive Plus to boost your thermostat’s savings – and get exclusive access to £60 bill credit with any fixed British Gas dual fuel tariff.
At present, I have no intention of changing my energy supplier, but come the summer or if my health or energy circumstances change, I might see what is available.
Will British Gas Develop A Hive For a Smaller Dwelling?
I suspect in ten years, if I’m still of this world, I shall be living in the following circumstances.
- Alone.
- In a two bedroom house, cottage or flat.
- Some form of probably electric central heating or perhaps even hydrogen.
- No car.
- A short walk to the bus stop and/or train station.
- Communal gardens to sit in.
- An Ocado style delivery for food, groceries and other essentials.
- A local gluten-free cafe.
- Full Wi-Fi
Perhaps, British Gas and others will develop a community for people like me?
HiiROC Partners With Siemens To Boost Clean Hydrogen Production
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from HiiROC.
These two bullet points, act as sub-headings.
-
HiiROC and Siemens sign a Memorandum of Understanding to provide advanced control technology and ensure the safe automation of hydrogen production.
-
HiiROC’s Thermal Plasma Electrolysis (TPE) process produces clean hydrogen and solid carbon, using significantly less electricity than water electrolysis and without creating carbon dioxide.
These five paragraphs explain the deal.
Clean hydrogen producer HiiROC, has partnered with technology company Siemens on its hydrogen production technology, helping customers to decarbonise their operations and support their Net Zero ambitions.
Under the agreement, HiiROC will leverage Siemens’ control technology and factory and automation expertise to ensure the safe, efficient automation of hydrogen production and support in scaling.
HiiROC’s proprietary Thermal Plasma Electrolysis (TPE) technology is designed to meet rising demand for low-cost, scalable solutions for clean hydrogen production at the point of use, which helps to significantly reduce costs by removing the need for specialised storage and transportation.
The TPE process disassembles gaseous hydrocarbons into hydrogen and solid carbon without creating carbon dioxide. This highly efficient process, recognised under the UK’s Low Carbon Hydrogen Standard, requires only a fifth of the electricity of water electrolysis.
As a key technology partner, Siemens will collaborate with HiiROC to advance product development, while its global developer support community will help in achieving the hydrogen producer’s international expansion goals. Siemens, which has ambitious commitments to decrease carbon emissions and contribute to a more sustainable society, works with organisations across sectors to decarbonise using technology.
Many chemical processes are all about brute force and very large amounts of energy. This marriage made in chemical heaven, is all about elegance and finesse.
The investors in HiiROC are not without substance and include Melrose Industries, HydrogenOne, Centrica, Hyundai and Kia.
I wrote more about HiiROC and a similar process in Centrica Partners With Hull-Based HiiRoc For Hydrogen Fuel Switch Trial At Humber Power Plant.