Unlocking Efficiency With Cryogenic Cooling Of GaN Traction Inverters
The title of this post, is the same as this insight on the Ricardo web site.
This is the introduction.
As the mobility sector accelerates toward zero-carbon propulsion, hydrogen fuel cell systems (HFCS) are emerging as a cornerstone technology for aviation, marine, and long-haul road transport. Among the most promising innovations in this space is the use of liquid hydrogen (LH₂) not only as a fuel source but also as a cryogenic coolant for electric powertrains. This dual-purpose approach offers transformative potential in system efficiency, packaging, and weight reduction—especially when paired with Gallium Nitride (GaN) semiconductors.
It is a very simple concept, but it appears to give worthwhile efficiency gains.
This was the article’s conclusion.
Ricardo’s cryogenic GaN inverter concept represents a bold leap toward ultra-efficient, lightweight, and integrated hydrogen propulsion systems. While challenges remain in materials, packaging, and reliability, the experimental results are compelling. With efficiencies nearing 99.8% and mass reductions over 50%, cryogenic cooling could redefine the future of electric mobility.
As the hydrogen economy matures, innovations like this will be pivotal in delivering clean, scalable, and high-performance solutions across all mobility sectors.
I very much suggest, that you take the time to read the whole insight.
Using The Concept In a Liquid Hydrogen Carrier
This Wikipedia entry describes the design and operation of an ocean-going liquid hydrogen carrier.
This is a paragraph.
Similar to an LNG carrier the boil off gas can be used for propulsion of the ship.
Ricardo’s concept would appear to be advantageous in the design of liquid hydrogen carriers and I would expect, it could also be applied to the design of LNG carriers.
I would not be surprised to see liquid hydrogen and LNG carriers were the first application of Ricardo’s concept.
This Wikipedia entry describes the Suiso Frontier, which is the world’s only liquid hydrogen carrier.
I believe that Ricardo’s concept could lead to the construction of a more of these ships. Will they mean that liquid hydrogen carriers will deliver hydrogen from sunny climes to places like Europe, Japan, Korea and Canada.
The concept would also enable efficient small liquid hydrogen carriers, that could deliver hydrogen on routes like the North of Scotland to Germany.
Using The Concept In A Railway Locomotive
I could see freight locomotives being designed as a large liquid hydrogen tank with appropriately-sized fuel cells and added electrical gubbins.
- They would be self-powered and would not require any electrification.
- They would be much quieter than current diesels.
- They could pull the heaviest freight trains, between Europe and Asia.
- They could even pull passenger trains, if an electrical hotel supply were to be arranged.
- They could be designed with very long ranges.
But above all they would be zero-carbon.
Note that I’ve written about long freight routes before.
- China, Russia And The EU’s Intermarium Bloc
- How To Move 100,000 Containers A Year Between Germany And China
- Georgia, Azerbaijan and Iran Discuss New Freight Corridor To link India And Europe
- Finland And Norway To Explore Building Arctic Rail Link
- A New Gateway To China: Europe Prepares For The Launch Of Baku–Tbilisi–Kars Railway
I believe that a long-distance liquid-hydrogen locomotive, that was based on the Ricardo concept, would be ideal for some of these routes.
A Specialised Hydrogen Delivery Train
In April 2022, I wrote The TruckTrain, where this is a simple description of the concept.
The Basic Design Concept
The leaflet on their web site describes the concept.
This visualisation at the bottom of the leaflet shows four TruckTrains forming a train carrying twelve intermodal containers, each of which I suspect are 20 feet long.
I believe that the TruckTrain concept could be converted into a hydrogen delivery train.
- It would be an appropriate length.
- It would be powered by the on-board hydrogen.
- The hydrogen would be stored as liquid hydrogen.
It would be able to go most places on the UK rail network.
Conclusion
Ricardo’s concept could revolutionise the use of hydrogen.
Centrica Secures Investment Stake In Gasrec Helping Boost UK Bio-LNG Ambitions
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica has secured a minority stake in Gasrec, the UK’s largest dual provider of bio-LNG (bio-Liquified Natural Gas) and bio-CNG (bio-Compressed Natural Gas) to the road transport sector,
These first two paragraphs give more details.
Gasrec says the investment will drive the next phase of its infrastructure ambitions, with plans to open a UK wide network of open-access refuelling stations supplying renewable bio-LNG for the decarbonisation of heavy goods vehicles.
Centrica is taking a 16% stake and becomes one of three major shareholders in Gasrec, alongside global integrated energy company bp and private family office 44 North.
I have some thoughts.
Does Running A Truck On bio-LNG or bio-CNG. Reduce Carbon Emissions?
This paragraph from the press release, gives the thoughts of Chris O’Shea, who is Group Chief Executive, Centrica.
Chris O’Shea, Group Chief Executive, Centrica plc, said: “Demand for bio-LNG for transport is growing fast as more HGV operators make the switch – drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel*. This investment in Gasrec enhances our collaboration with the leading company in the sector, and puts us in a strong position to energise a vital sector of the industry on its journey to net zero.”
As Centrica is a public company, with shareholders, who would take a dim view of Mr. O’Shea telling porkies, I suspect we can assume that the following is true.
Drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel.
The asterisk in the full quote, refers to this note.
Low Carbon Vehicle Partnership, Innovate UK and Office for Low Emission Vehicles, Low Emission Freight & Logistics Trial (LEFT), Key Findings, November 2020. Using specific feedstocks CO2 reductions of 200% are achievable.
Centrica could be being conservative with their claims.
Decarbonising Buses, Locomotives And Trucks
Despite what Elon Musk, would have us believe, electric trucks will not dominate the future of freight transport.
An electric truck would be the vehicle equivalent of asking Usain Bolt to run a hundred metres with a large refrigerator on his back.
Trucks are going to need a fuel without a weight penalty and with a long range.
I asked Google for information about Cummins diesel, natural gas and hydrogen engines and received this AI Overview.
Cummins offers engines powered by diesel, natural gas, and hydrogen. While diesel engines are well-established, Cummins is also developing both natural gas and hydrogen engines, particularly focusing on hydrogen as a pathway to zero-carbon solutions for various applications. Cummins utilizes a fuel-agnostic platform, meaning a common base engine can be adapted for different fuel types, including diesel, natural gas, and hydrogen.
Recently, GB Railfreight purchased thirty Class 99 locomotives from Stadler.
- They can use electrification, where it exists.
- Where electrification doesn’t exist, they can use an onboard Cummins diesel engine, which is built in Darlington.
- In electric-mode, they have 6.2 MW of power, and are the most powerful locomotives ever to run on UK railways.
- In diesel-mode, they have 1.8 MW of power, which is more than enough to haul a large container train in and out of Felixstowe.
I had thought that at some future date, Cummins would convert these locomotives to electro-hydrogen.
But now that Gasrec is providing bio-LNG and bio-CNG, GB Railfreight, have the option of converting both hydrogen and biomethane.
Similar logic can be applied to Wrightbus’s Streetdeck Ultroliner, one version of which is fitted with a Cummins engine, that can be converted to electric, hydrogen or natural gas, which of course includes biomethane. This page on the Wrightbus web site describes the bus.
Wrightbus are also going back into coach manufacture, as I wrote about in Wrightbus Goes Back To The Future As It Relaunches The Contour Coach. As with the Streetdeck Ultroliner, Cummins seem to be providing one of the power units.
It seems to me, that the zero- and low-carbon revolution in transport will generate a need for the availability of biomethane, hydrogen and natural gas fuel for transport all over the country.
Gasrec with around twenty biomethane fuelling points around the country, seem well-placed to supply the biomethane in bio-LNG or bio-CNG form.
Could Gasrec Deliver Hydrogen?
Various bus companies in the UK, have had difficulty getting the fuel for their hydrogen buses.
I believe that delivering hydrogen would be very similar to delivering LNG and if Gasrec can deliver LNG successfully and safely, they probably have the technology to do the same for hydrogen.
Centrica Seem To Be Assembling An Interesting Consortium
These are some deals, that I have reported on this blog, that involve Centrica.
- Centrica, along with Hyundai, Kia, Siemens and others have backed Hull-based hydrogen start-up; HiiROC, who can produce affordable hydrogen from any hydrocarbon gas including natural gas, where it is needed.
- Centrica have invested in Sizewell C. Will they be using their share of the electricity to make affordable pink hydrogen using HiiROC?
- In Centrica And Ryze Agree To Develop Hydrogen Pathway, I talked about how Centrica and Ryse were aiming to bring hydrogen to the masses.
- In Recurrent Energy’s Middle Road Project Sold To Centrica, I talked about a Centrica investment in solar power.
- In Aberdeen’s Exceed Secures Centrica Rough Contract, I talked about how Centrica were redeveloping the Rough gas storage site for hydrogen.
- In Lhyfe And Centrica To Develop Offshore Renewable Green Hydrogen In The UK, I talked about developing offshore hydrogen.
- In Centrica Announces Hydrogen Ready Combined Heat And Power Partnership With 2G, the title says it all.
- In Centrica Signs UK Biomethane Agreement With Yorkshire Water And SGN Commercial Services, Centrica appear to be sourcing biomethane from Yorkshire Water.
- In Centrica Invests In Renewable Energy Storage Capabilities To Boost UK’s Energy Security And Accelerate Transition To Net Zero, I talk about Centrica, Goldman Sachs and others, investment in liquid-air energy storage company; Highview Power.
- In British Gas Owner Mulls Mini-Nuke Challenge To Rolls-Royce, I talk about rumours that Centrica might invest in SMRs.
Note.
- A lot of these deals are are about hydrogen production.
- Some of these deals are about biomethane production.
- None of these deals talk about getting hydrogen and biomethane to customers.
It appears to me, that Gasrec have a model that works to get hydrogen, methane and biomethane from production and storage to the end customers.
Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network
In Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network, I talked about supplying all those millions of off-gas grid properties with hydrogen for heating, agricultural and industrial purposes, in the countryside of the UK.
Gasrec have the technology to decarbonise the countryside.
Conclusion
Gasrec would appear to be a very useful partner for Centrica.
An Interesting Comment From Lord Peter Hendy
This article on Modern Railways is entitled Chiltern FINALLY Signs Mk 5 Deal.
This extract from the article describes the deal.
An agreement for Chiltern Railways to lease the Mk 5A coaches previously operated by TransPennine Express and owned by Beacon Rail Leasing has been signed – and the trains are due to replace the current Mk 3 stock in phases from 2026. A 10-year lease has been agreed for the vehicles.
Chiltern will take on all 13 five-car sets as well as the spare Driving Trailer and the dedicated pool of 14 Class 68 locomotives.
The article also, has this excellent quote from Lord Peter Hendy, who is the Rail Minister at the end.
This government is putting passengers back at the heart of the 21st century railway by investing to make journeys easier, greener, and more comfortable.
“We are continuing to support Chiltern as they develop a plan to introduce additional services into their timetable, giving people more opportunities to work, live, and socialise.
I agree with much of what Lord Peter Hendy says, but could we see some actions to back up the words.
I have a few thoughts.
Lumo To Glasgow
I wrote about this new service in Lumo Will Extend Its King’s Cross And Edinburgh Service To Glasgow.
Given the opposition of the Transport Minister to open access services, I didn’t think this innovative service would be approved.
- But it does add an affordable passenger-friendly service to London and Glasgow routes.
- It will certainly be an easier route to London for some in Scotland.
- It also adds some much-needed direct services between Newcastle and Glasgow.
Did Lord Peter Hendy have words to help Lumo get its approval?
As I wrote in Could London And Central Scotland Air Passengers Be Persuaded To Use The Trains?, I also believe that this new Lumo service could persuade more air passengers to take the train to Scotland.
Lumo To Stirling
I wrote about this service in ORR: Open Access Services Given Green Light Between London And Stirling.
- First Group has taken over Grand Union Trains and the service will now be run by Lumo, who will use diesel Class 222 trains.
- But Lumo will have the option of running their electric Class 803 trains on the route, as it is fully electrified, when their fleet receives more trains.
This was another service, that I didn’t think would be approved, as no other services on the West Coast Main Line were approved, as Network Rail objected.
But it certainly meets the words in Lord Peter Hendy’s statement.
Like Lumo’s service to Glasgow, when the Stirling service gets electric trains, it will surely cut carbon emissions of travellers to Central Scotland.
Chiltern’s Replacement Trains
Chiltern Railways are replacing this fleet of locomotive hauled trains.
- 8 Class 68 locomotives
- 25 Mark 3 coaches
- 6 Driving Van Trailers
As services between London Marylebone and Birmingham Moor Street stations consist of one locomotive, five coaches and one driving van trailer, that means there are two spare locomotives, one spare coach and one spare driving van trailer, if there are five rakes of coaches in service.
The new fleet will be.
- 14 Class 68 locomotives
- 52 Mark 5A coaches
- 14 Driving Van Trailers
If services between London Marylebone and Birmingham Moor Street stations consist of one locomotive, four coaches and one driving van trailer, that means there are one spare locomotive and one spare driving van trailer, which gives a possible thirteen rakes of coaches in service.
There are certainly enough to expand Chiltern’s services. The obvious destination would surely be Oxford. These pictures show the two North-pacing platforms at Oxford station.
The platforms would be shared with East-West Rail, but they are around 160 metres in length.
The Modern Railways article quote Arriva Group Managing Director UK Trains Amanda Furlong as saying this.
Upgrading our fleet is a vital next step in Chiltern’s modernisation plans and an important part of Arriva’s wider ambition to support the transition to more sustainable rail travel across the UK and Europe.
We are proud to support this important milestone for Chiltern Railways, which is a great example of what can be achieved through strong collaboration with Government to deliver practical improvements for passengers. We look forward to seeing these upgraded trains improve journeys and lower emissions across the network.
She certainly would agree on some issues with Lord Peter Hendy.
So will Chiltern Railways do something to reduce the carbon footprint of their fourteen Class 68 locomotives?
- The Class 68 locomotives don’t have too many miles on the clock.
- Chiltern have already run some their Class 68 locomotives on HVO, so this must be a possibility.
- In total there are thirty-four Class 68 locomotives in service all of which have Caterpillar engines, so a conversion to zero-carbon power could be worthwhile.
I asked Google for an AI Overview on How many diesel locomotives have caterpillar engines worldwide? I got this answer.
While a precise worldwide count of diesel locomotives powered by Caterpillar (CAT) engines is difficult to pinpoint, it’s estimated that hundreds, if not thousands, of locomotives are equipped with CAT engines. Caterpillar has a long history of supplying engines to the rail industry, with engines like the 3500 series powering both mainline and switcher locomotives. Additionally, CAT engines are also used in generator sets for Head End Power (HEP) in passenger locomotives.
Note.
- It appears that, Caterpillar might have given up making truck engines because of emission issues.
- London Marylebone and Oxford is 66.8 miles
- London Marylebone and Birmingham Snow Hill is 112.3 miles.
Perhaps one of the consultants like Ricardo could convert these locomotives to run on hydrogen.
Centrica Really Can’t Lose At Sizewell
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica’s £1.3 billion investment in Sizewell C guarantees substantial returns, even with cost overruns.
These two-and-a-half paragraphs explain the funding.
Now we know what Ed Miliband means by his “golden age of nuclear” — golden for the companies putting their money into Sizewell C. Yes, reactor projects have a habit of blowing up private investors. But maybe not this one. It looks more like an exercise in transferring risk to consumers and the taxpayer.
Sure, nobody builds a £38 billion nuke on a Suffolk flood plain without a frisson of danger. But the energy secretary and his Treasury chums have done their bit to make things as safe as possible for the companies putting in equity alongside the government’s 44.9 per cent stake: Canada’s La Caisse with 20 per cent, British Gas-owner Centrica (15 per cent), France’s EDF (12.5 per cent) and Amber Infrastructure (7.6 per cent).
For starters, nearly all the debt for the 3.2 gigawatt plant, three-quarters funded by loans, is coming from the state-backed National Wealth Fund. It’s bunging in up to £36.6 billion, with £5 billion more guaranteed by a French export credit agency.
It looks to me that between them the British and French governments are providing £41.5 billion of loans to build the £38 billion nuke.
These are my thoughts.
Hydrogen And Sizewell C
This page on the Sizewell C web site is entitled Hydrogen And Sizewell C.
Under a heading of Hydrogen Buses, this is said.
At Sizewell C, we are exploring how we can produce and use hydrogen in several ways. We are working with Wrightbus on a pilot scheme which, if successful, could see thousands of workers transported to and from site on hydrogen double decker buses. You can read more about the pilot scheme in our press release
Firstly, it could help lower emissions during construction of the power station. Secondly, once Sizewell C is operational, we hope to use some of the heat it generates (alongside electricity) to make hydrogen more efficiently.
This would appear to be a more general statement about hydrogen and that the following is planned.
- Hydrogen-powered buses will be used to bring workers to the site. A press release on the Sizewell C web site, talks about up to 150 buses. That would probably be enough buses for all of Suffolk.
- Hydrogen-powered construction equipment will be used in the building of the power station.
- It also talks about using the excess heat from the power station to make hydrogen more efficiently. I talk about this process in Westinghouse And Bloom Energy To Team Up For Pink Hydrogen.
This is a substantial investment in hydrogen.
Centrica And Electricity From Sizewell C
The article in The Times, also says this.
Even so, there’s a fair bit of protection for the likes of Centrica, which has also agreed a 20-year offtake deal for its share of Sizewell’s electricity. The price of that is not yet known.
Nothing is said in the article about the size of Centrica’s electricity offtake.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell C, that would by 480 MW.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell B + C, that would by 660 MW.
If they use their share to generate hydrogen, Suffolk would have a massive hydrogen hub.
To power the buses and construction of Sizewell C, Sizewell B could be used to provide electricity to create the hydrogen.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Produced?
Centrica, along with other companies, who include Hyundai and Kia, are backers of a company in Hull called HiiROC, who use a process called Thermal Plasma Electrolysis to generate hydrogen.
On their web site, they have this sub-heading.
A Transformational New Process For Affordable Clean Hydrogen
The web site also describes the process as scalable from small modular units up to industrial scale. It also says this about the costs of the system: As cheap as SMR without needing CCUS; a fraction of the energy/cost of water electrolysis.
If HiiROC have achieved their objective of scalability, then Centrica could grow their electrolyser to meet demand.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Distributed?
Consider.
- Currently, the Sizewell site has both road and rail access.
- I can still see in my mind from the 1960s, ICI’s specialist articulated Foden trucks lined up in the yard at Runcorn, taking on their cargoes of hydrogen for delivery all over the country.
- As that factory is still producing hydrogen and I can’t remember any accidents in the last sixty years, I am fairly sure that a range of suitable hydrogen trucks could be developed to deliver hydrogen by road.
- The road network to the Siewell site is being updated to ensure smooth delivery of workers and materials.
- The rail access to the Sizewell site is also being improved, for the delivery of bulk materials.
I believe there will be no problems delivering hydrogen from the Sizewell site.
I also believe that there could be scope for a special-purpose self-propelled hydrogen tanker train, which could both distribute and supply the hydrogen to the vehicles, locomotives and equipment that will be using it.
Where Will The Hydrogen Be Used?
I have lived a large part of my life in Suffolk and know the county well.
In my childhood, there was quite a lot of heavy industry, but now that has all gone and employment is based on agriculture, the Port of Felixstowe and service industries.
I can see hydrogen being used in the following industries.
Transport
Buses and heavy trucks would be powered by hydrogen.
The ports in the East of England support a large number of heavy trucks.
Large Construction Projects
Sizewell C is not the only large construction project in the East of England, that is aiming to use low-carbon construction involving hydrogen. In Gallagher Group Host Hydrogen Fuel Trial At Hermitage Quarry, I talked about a hydrogen fuel trial for the Lower Thames Crossing, that involved JCB and Ryse Hydrogen.
Hydrogen for the Lower Thames Crossing could be delivered from Sizewell by truck, down the A12.
Rail
We may not ever see hydrogen-powered passenger trains in this country, but I do believe that we could see hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
Consider.
- The latest electro-diesel Class 99 locomotives from Stadler have a Cummins diesel engine.
- The diesel engine is used, when there is no electrification.
- Cummins have developed the technology, that allows them to convert their latest diesel engines to hydrogen or natural gas power, by changing the cylinder head and the fuel system.
- Access to the Port of Felixstowe and London Gateway needs a locomotive with a self-powered capability for the last few miles of the route.
A Class 99 locomotive converted to hydrogen would be able to run with out emitting any carbon dioxide from Felixstowe or London Gateway to Glasgow or Edinburgh.
Ports
Ports have three main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for port workers.
- To fuel ships of all sizes from the humblest work-boat to the largest container ships.
- There may need to be fuel for hydrogen-powered rail locomotives in the future.
There are seven ports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth, Harwich, Ipswich, London Gateway, Lowestoft and Tilbury.
The proposed Freeport East is also developing their own green hydrogen hub, which is described on this page on the Freeport East web site.
Airports
Airports have two main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for airport workers.
- In the future, there is likely to be hydrogen-powered aircraft.
There are three airports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Norwich, Southend and Stansted.
Agriculture And The Rural Economy
Agriculture and the rural economy would be difficult to decarbonise.
Consider.
- Currently, most farms would use diesel power for tractors and agricultural equipment, which is delivered by truck.
- Many rural properties are heated by propane or fuel oil, which is delivered by truck.
- Some high-energy rural businesses like blacksmiths rely on propane, which is delivered by truck.
- Electrification could be possible for some applications, but ploughing the heavy land of Suffolk, with the added weight of a battery on the tractor, would probably be a mathematical impossibility.
- JCB are developing hydrogen-powered construction equipment and already make tractors.
- Hydrogen could be delivered by truck to farms and rural properties.
- Many boilers can be converted from propoane to run on hydrogen.
I feel, that hydrogen could be the ideal fuel to decarbonise agriculture and the rural economy.
I cover this application in detail in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Exports
Consider.
- Sizewell B and Sizewell C nuclear powerstations have a combined output of 4.4 GW.
- A rough calculation shows that there is a total of 7.2 GW of wind farms planned off the Suffolk coast.
- The East Anglian Array wind farm alone is said in Wikipedia to be planned to expand to 7.2 GW.
- The Sizewell site has a high capacity connection to the National Grid.
Nuclear plus wind should keep the lights on in the East of England.
Any excess electricity could be converted into hydrogen.
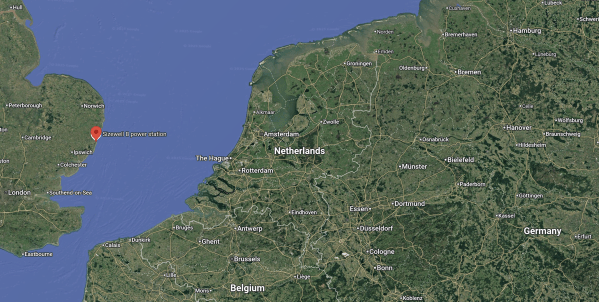
This Google Map shows the location of Sizewell B in relation to Belgium, Germany and The Netherlands.
The Sizewell site is indicated by the red arrow.
The offshore oil and gas industry has used technology like single buoy moorings and coastal tankers to collect offshore natural gas for decades.
I don’t see why coastal hydrogen tankers couldn’t export excess hydrogen to places around the North Sea, who need the fuel.
It should be born in mind, that Centrica have a good reputation in doing natural gas trading. This expertise would surely be useful in hydrogen trading.
Conclusion
I believe that a hydrogen hub developed at Sizewell makes sense and I also believe that Centrica have the skills and technology to make it work.
Do Rolls-Royce mtu Have A Plan To Decarbonise Their Diesel Engines For Rail Applications?
Data Sheets For Rolls-Royce mtu Diesel Engines For Trains
These are data sheets for various Rolls-Royce mtu diesel engines that can be used in rail applications.
Rolls-Royce Releases mtu Rail Engines For Sustainable Fuels
The title of this section, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
These four bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- mtu Series 1300, 1500 and 1800 engines already released; Series 1600 and 4000 to follow shortly
- Up to 90% CO2 savings by operating existing engines with Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO/renewable diesel)
- Locally emission-free operation possible in combination with mtu Hybrid PowerPack
- Field tests with DB Cargo and RDC Autozug Sylt
This is the first paragraph.
Rolls-Royce is taking a significant step towards even more climate-friendly rail transport with the release of mtu rail engines for use with sustainable fuels. With synthetic diesel fuels of the EN15940 standard, CO2 emissions can be reduced by up to 100 percent compared to fossil diesel. Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO or renewable diesel), which is already commercially available today, reduces CO2 emissions by up to 90 percent. If the fuels are produced with the help of renewable energy and green hydrogen – through what is termed a Power-to-X process – existing rail vehicles can be operated in a completely CO2-neutral manner. The mtu Series 1800 engines which are used in mtu PowerPacks, as well as Series 1300 and 1500 for locomotives and multi-purpose vehicles, are already approved for use with synthetic fuels such as HVO. Series 1600 and versions of Series 4000 engines will follow in the near future. The release of engines for climate-friendly fuels requires a series of tests and trials and Rolls-Royce has found strong partners for this activity. DB Cargo and RDC Autozug Sylt have already tested or are currently testing mtu Series 4000 engines with HVO in their locomotives.
How Does That Fit With The UK’s Population Of Rolls-Royce mtu Diesel Engines?
These classes of train have Rolls-Royce mtu engines.
- Class 43 power cars – 6V 4000 R41R
- Class 168 train – 6R 183 TD 13H
- Class 170 train – 6R 183 TD 13H
- Class 172 train – 12V 1800 R83
- Class 195 train – 12V 1800 R85L
- Class 196 train – 12V 1600 R85L
- Class 197 train – 12V 1600 R85L
- Class 800 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 801 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 802 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 805 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 810 train – 12V 1600 R80L
Note.
- Class 168 and 170 trains seem to be powered by older model Rolls Royce mtu engines.
- Class 180, 220,221 and 222 trains are powered by Cummins engines.
- I can’t find what engines power Class 805 and 810 trains, but it is reasonable to assume they have the same engines as the other Hitachi trains.
- As CAF are building LNER’s new tri-mode trains, I suspect these trains will also have Rolls Royce mtu engines.
It would appear that all the Rolls-Royce mtu rolling stock in the UK, with the possible exception of the Class 168 and 170 trains will be able to run on sustainable fuels.
Rolls Royce mtu And Hydrogen
This press release from Rolls-Royce is entitled Rolls-Royce Successfully Tests mtu Engines With Pure Hydrogen.
This is the first paragraph.
Rolls-Royce today announces that it has conducted successful tests of a 12-cylinder gas variant of the mtu Series 4000 L64 engine running on 100% hydrogen fuel. The tests, carried out by the Power Systems business unit, showed very good characteristics in terms of efficiency, performance, emissions and combustion. These tests mark another important step towards the commercial introduction of hydrogen solutions to meet the demand of customers for more sustainable energy.
Engines of mtu’s 4000 family are used in Class 43 power cars, so surely these developments could lead to hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
The picture shows a Class 43 power car at Glasgow Queen Street station.
Could Rolls-Royce mtu hydrogen power keep these iconic trains running for a few more years?
In ‘Spirit of Innovation’ Stakes Claim To Be The World’s Fastest All-Electric Vehicle, I look at Rolls-Royce’s Spirit of Innovation, which set the record for an electric vehicle at 555.9 km/hour.
As the InterCity125 already holds the record for the fastest diesel train, perhaps Rolls-Royce will attempt to set a record for the fastest hydrogen-powered train?
Decarbarbonising The CAF Class 195, 196 And 197 Trains
If Rolls-Royce mtu develop a hydrogen version of the 1800 diesel engine, then this could be used to fully decarbonise the CAF trains.
The operators may consider it’s not worth it and continue with using sustainable fuels.
But the possibility is surely there.
There must also be the possibility of developing a fuel cell replacement for the 1800 diesel, that can be slotted into the train.
Decarbarbonising The Hitachi Class 80x Trains
Hitachi are developing battery packs and the data sheet can be downloaded from this page on the Hitachi web site.
Decarbarbonising The CAF Tri-Mode Trains
I feel that as CAF usually use Rolls-Royce mtu engines, I suspect these trains will be designed, so they can be converted to hydrogen.
Conclusion
Rolls-Royce mtu appear to be on a path to decarbonise all their diesel engines.
Global First For Formula 1: CEVA Logistics Transports Ferrari Equipment By Rail
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Container News.
This is the sub-heading.
CEVA Logistics, CMA CGM-owned third-party logistics provider, recently designed an innovative rail transport solution for Scuderia Ferrari’s F1 racing team in North America
These paragraphs outline the transport.
In a global first for Formula 1, Ferrari equipment is being transported by rail between three North American F1 grand prix races as part of the two companies’ efforts to cut carbon emissions.
Since the start of their cooperation in 2022, CEVA has been altering the Scuderia Ferrari logistics programme. As CEVA guarantees that the equipment reaches each of the 23 Grand Prix racing venues on schedule, the flow of the six different 45-ton equipment kits that travel the world has shifted away from air freight and toward a primary combination of ocean and road freight.
Carbon savings were 90 % compared to flying and 32 % compared to an all-road route.
But as the containers appeared to have travelled 4,000 miles between Montreal to Las Vegas via Austin, probably hauled by a diesel locomotive, how much extra carbon savings could have been achieved if a hydrogen-powered locomotive had been used?
Nestlé And Tesco Launch Double-Stacked Rail Freight Trial
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Logistics Manager.
This is the sub-heading.
Nestlé UK and Ireland has successfully completed its first delivery to supermarket chain Tesco using a ‘first-of-its-kind’ rail container, as part of a new rail freight trial.
These are the first three paragraphs.
The container features a roof-raising mechanism allowing products to be “double-stacked from floor to ceiling operating at full capacity before the roof is lowered for transit”. The appeal of this is its capability to store potentially twice as much freight in one journey, reducing costs and emissions.
This is part of Nestlé’s plans to increase freight capacity on trains as a means of reducing the negative impact that the company’s logistics operations have on the environment. It is hoped that the trial will allow the process to be refined over time, providing further opportunities for Nestlé to expand the volume of goods that can be transported via rail in a single shipment.
This focus is integral to Nestlé’s strategy to reduce its reliance on the consumption of diesel in its road transport network. According to a 2021 report from the Rail Delivery Group, rail freight produces, on average, 76% fewer emissions than road transport. This, it claims, equates to a reduction of around 1.4 million tonnes of CO₂ nationally each year.
Note.
- This article would appear to be a follow-on to Nestlé Unveils New Double-Stacking Rail Logistics Plan To Reduce Carbon Footprint, which I wrote in June 2022.
- In From 2025, Nestlé Waters France Will Use The First Hydrogen-Powered Freight Train Through An Innovative Solution Developed by Alstom and ENGIE, I talk about how Nestlé are experimenting with hydrogen-powered locomotives.
Nestlé certainly seem to be working on reducing the carbon dioxide produced by their logistic operations.
Electrification Between Newbury And East Somerset Junction
In the August 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled GWR Seeks Opportunities To Grow.
This is the sub-heading.
Managing Director Mark Hopwood tells Philip Sherratt there is plenty of potential to increase rail’s economic contribution.
This is two paragraphs.
The desire to provide electrification to support aggregates traffic from the Mendip quarries could also benefit GWR , says Mr. Hopwood. ‘Having an electric loco would massively help with pathing heavy freight trains through the Thames Valley. If you could electrify from Newbury to East Somerset Junction, a big chunk of the Berks and Hants route would be wired.
Then you can ask how much further you could get on battery power on an IET without running out of juice.’
I have some thoughts.
Where Is East Somerset Junction?
This OpenRailwayMap shows East Somerset junction.
Note.
- The East Somerset junction is marked with the blue arrow.
- East Somerset junction is 5.2 miles North of Bruton station and 5.4 miles South of Frome station on the Reading and Taunton Line.
As the map shows there is a branch to Merehead Rail Sidings, which is shown in yellow.
This Google Map shows Merehead Rail Sidings.
Note.
- It looks like there is a massive quarry to the North of the A361 road, which curves across the map.
- It is labelled Torr Works – Aggregate Industries.
- Torr Works has a Wikipedia entry.
- The rail sidings are South of the A361.
- Zooming in on the map, shows that the railway between East Somerset junction and Merehead is single-track and only a few miles long.
Distances from East Somerset junction are as follows.
- Dorchester junction – 41.2 miles
- Newbury – 53.4 miles
- Taunton – 37.2 miles
- Weymouth – 47.8 miles
Note that it is electrified with 750 VDC third-rail between Weymouth and Dorchester junction.
Range of Battery-Electric Trains
Consider.
- A Bombardier engineer told me eight years ago, that the battery-electric Class 379 train had a range of sixty miles.
- Stadler’s FLIRT Akku has a Guinness world record of 139 miles on one battery charge. See this page on the Stadler web site.
- Even Stadler’s Class 777 trains for Merseyrail have a range of 84 miles on battery power. See New Merseyrail Train Runs 135 km On Battery.
It does appear that five-car battery-electric trains will have ranges in excess of a hundred miles.
I believe that because Hitachi’s battery makers have a good record, they will probably be very ambitious and will want that Guinness record, that Hitachi’s Class 802 trains will have a battery range not far short of the 139 miles of the Stadler FLIRT Akku.
I will be very surprised if Hitachi’s battery-electric version of a Class 802 train, doesn’t have range of at least 125 miles.
But say if they could do say 140 miles, the battery-electric Class 802 train could cover every long-distance route in the UK, which would attract orders for trains to run on the following routes.
- Cardiff and Swansea
- Crewe and Holyhead
- Edinburgh and Aberdeen
- Edinburgh and Inverness
- Crewe and Holyhead
- London Waterloo and Exeter St. Davids
A substantial reward to the battery makers, would probably not be out of order.
Aggregate Trains From The Mendips
Consider.
- Mining and quarrying companies are under pressure from governments, shareholders and environmentalists to reduce their carbon footprints.
- Many are replacing diesel-powered mining excavators and trucks, with electric or hydrogen versions.
- In addition, those companies delivering building products to the construction industry are under pressure to provide low-carbon products.
- Using rail with electric traction to deliver products to market would cut carbon emissions and might even help sales.
These Mendip quarries appear to be connected to the Reading and Taunton Line.
- Torr Works – Connects 5.4 miles to the South of Frome.
- Whatley Quarry – Connects close to Frome.
There may be others.
But these rail-connected quarries, connect at or North of East Somerset junction, to where Mark Hopwood is proposing electrification.
Zero-carbon rail traction could even be possible, by electrifying the short single-track branch lines. or by using hydrogen-electric hybrid locomotives.
GWR’s London And South-West Services
These services use the Reading and Taunton Line to join the Bristol and Exeter Line at Taunton, before going on to Exeter, Plymouth and other destinations in the South-West of England.
These are distances from East Somerset Junction.
- Exeter – 67 miles
- Paignton 95.2 miles
- Penzance – 198.5 miles
- Plymouth – 119.0 miles
- Taunton – 37.2 miles
Note.
- Exeter, Paignton, Penzance and Plymouth stations would need short lengths of electrification to charge terminating trains or top-up passing trains.
- In Thoughts About Electrification Through Devon And Cornwall, I showed that the average stop time at Plymouth station was eight minutes, which could be enough for the rail equivalent of a Formula One splash and dash.
- A 125 mile battery range, not only enables London and Penzance, but also Cardiff and Swansea, and Edinburgh and Aberdeen, when the extra electrification is completed.
Could my estimate of a 125 mile battery range, be Hitachi’s objective for their battery-electric trains?
The Ultimate Battery-Electric Class 802 Train
Hitachi have been totally silent on how the fitting of batteries to Class 802 trains is going.
But Mark Hopwood is more forthcoming in the GWR Seeks Opportunities To Grow article. where this is said.
Meanwhile, GWR had announced plans with Eversholt Rail to trial the replacement of a diesel generator unit with batteries on a Class 802 IET. However, Mr. Hopwood says this would not be useful for GWR and so the trial is not proceeding; instead, a TransPennine Express Class 802 will be the subject of a battery trial.
It sounds to me that another solution is being developed to get trains to run on electric power between London and the South-West.
- I think we can rule out full electrification on the grounds of cost, disruption, time and the Nimbys and objectors will have a field day.
- Newbury and Penzance is a distance of 251.9 miles, which would surely need a lot of batteries.
Mark Hopwood’s idea to electrify the 53.4 miles between Newbury And East Somerset junction, is starting to look like a good compromise.
GWR’s Bristol/Gloucester And Weymouth Services
These stopping trains are run by diesel trains and take the following route between Bristol Temple Meads and Weymouth stations.
- Keynsham
- Oldfield Park
- Bath Spa
- Freshford
- Avoncliff
- Bradford-on-Avon
- Trowbridge
- Westbury
- Frome
- East Somerset junction
- Bruton
- Castle Cary
- Yeovil Pen Mill
- Thornford
- Yetminster
- Chetnole
- Maiden Newton
- Dorchester West
- Dorchester junction
- Upwey
Note.
- I would assume that there is enough electrification at Bristol Temple Meads and towards Gloucester to charge the trains.
- Trains would leave Bristol Temple Meads with a full battery.
- The eighteen stops mean that an electric train with regenerative braking will be more efficient.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury is not electrified.
- Westbury and East Somerset junction will be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead electrification under Mark Hopwood’s proposal.
- Trains take sixteen minutes between Westbury and East Somerset junction.
- East Somerset junction and Dorchester junction is not electrified.
- Dorchester junction and Weymouth is electrified with 750 VDC third-rail electrification.
- Trains take ten minutes between Dorchester junction and Weymouth.
Distances of the various legs are as follows.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury – 28.3 miles – Not Electrified
- Westbury and East Somerset junction – 11.4 miles – Electrified
- East Somerset junction and Dorchester junction – 41.4 miles – Not Electrified
- Dorchester junction and Weymouth – 6.6 miles – Electrified
The two sections without electrification, should be well within range of a dual-voltage battery-electric train, that has been designed for the route.
GWR’s Cardiff Central And Portsmouth Harbour Service
These stopping trains are run by diesel trains and take the following route between Bristol Temple Meads and Portsmouth Harbour stations.
- Keynsham
- Oldfield Park
- Bath Spa
- Freshford
- Avoncliff
- Bradford-on-Avon
- Trowbridge
- Westbury
- Warminster
- Salisbury
- Romsey
- Redbridge
- Southampton Central
- Fareham
- Cosham
- Fratton
- Portsmouth & Southsea
Note.
- I would assume that there is enough electrification at Bristol Temple Meads and towards Cardiff Central to charge the trains.
- Trains would leave Bristol Temple Meads with a full battery.
- The seventeen stops mean that an electric train with regenerative braking will be more efficient.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury is not electrified.
- Westbury station will be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead electrification under Mark Hopwood’s proposal.
- Trains would leave Westbury with a full battery.
- Westbury and Redbridge is not electrified.
- Redbridge and Portsmouth Harbour is electrified with 750 VDC third-rail electrification.
Distances of the various legs are as follows.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury – 28.3 miles – Not Electrified
- Westbury and Redbridge – 46.4 miles – Not Electrified
- Redbridge and Portsmouth Harbour – 28.5 miles – Electrified
The two sections without electrification, should be well within range of a dual-voltage battery-electric train, that has been designed for the route.
GWR’s Bristol Temple Meads And Salisbury Services
These stopping trains are run by diesel trains and take the following route between Bristol Temple Meads And Salisbury stations.
- Keynsham
- Oldfield Park
- Bath Spa
- Freshford
- Avoncliff
- Bradford-on-Avon
- Trowbridge
- Dilton Marsh
- Warminster
Note.
- I would assume that there is enough electrification at Bristol Temple Meads to charge the trains.
- Trains would leave Bristol Temple Meads with a full battery.
- An electric train with regenerative braking will be more efficient.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury is not electrified.
- Westbury station will be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead electrification under Mark Hopwood’s proposal.
- Trains would leave Westbury with a full battery.
- Westbury and Salisbury is not electrified.
Distances of the various legs are as follows.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury – 28.3 miles – Not Electrified
- Westbury and Salisbury – 24.4 miles – Not Electrified
The two sections without electrification, should be well within range of a battery-electric train, that has been designed for the route.
GWR’s Swindon And Westbury Services
These stopping trains are run by diesel trains and take the following route between Swindon and Westbury stations.
- Chippenham
- Melksham
- Trowbridge
Note.
- This is the Transwilts service.
- I would assume that there is enough electrification at Swindon to charge the trains.
- Trains would leave Swindon with a full battery.
- An electric train with regenerative braking will be more efficient.
- Chippenham and Westbury is not electrified.
- Westbury station will be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead electrification under Mark Hopwood’s proposal.
- Trains would leave Westbury with a full battery.
Distances of the various legs are as follows.
- Swindon and Chippenham – 16.9 miles – Electrified
- Chippenham and Westbury – 15.8 miles – Not Electrified
The section without electrification, should be well within range of a battery-electric train, that has been designed for the route.
What Can Be Done If The Electrification Is Not Long Enough?
Some of these routes battery-electric routes may need more electrification to work efficiently.
Despite some routes having both 25 KVAC overhead and 750 VDC third-rail electrification, any extension of the electrification would be overhead, as new third-rail electrification is effectively banned.
Conclusion
It looks like Mark Hopgood proposal is an excellent idea to enable the decarbonisation of GWR services in Wiltshire and Somerset.
- Express services would be run by battery-electric Class 802 trains.
- Local services would be run by battery-electric trains with perhaps three cars.
Some of the local trains would need to be dual-voltage to use both forms of electrification.
Hydrogen ‘The Only Option’ For Metrobus Fastway ZE
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Route One.
This is the introductory paragraph.
Hydrogen fuel cell-electric remains the most realistic zero-emission technology for usage cases requiring very high mileage and utilisation capabilities. That is the verdict from the Go-Ahead Group after its Metrobus subsidiary launched 20 Wrightbus GB Kite Hydroliner single-deckers on 29 June.
This paragraph gives more details.
Go-Ahead Group Chair Claire Hollingsworth, who was present at the launch alongside Under-Secretary of State for Transport Richard Holden and other stakeholders and dignitaries, underlines the need for hydrogen on Fastway. “These are the most intensive routes in the Go-Ahead network,” she explains. “We need 300 miles of range and have little time to plug in.”
Let’s face it, a bus that takes a lot of time to fuel-up can’t be as efficient, as one that takes just a few minutes. Especially, if the buses are running a large number of hours per day.
The whole article is a must read and surely Go-Ahead’s conclusion to other modes of transport, that do long distances, like heavy trucks, long-distance coaches and railway locomotives.